Mutation causing congenital myasthenia reveals acetylcholine receptor beta/delta subunit interaction essential for assembly
- PMID: 10562302
- PMCID: PMC409847
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI8179
Mutation causing congenital myasthenia reveals acetylcholine receptor beta/delta subunit interaction essential for assembly
Abstract
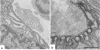
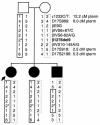
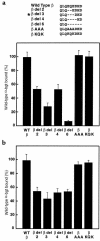
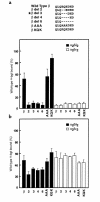
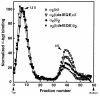
We describe a severe postsynaptic congenital myasthenic syndrome with marked endplate acetylcholine receptor (AChR) deficiency caused by 2 heteroallelic mutations in the beta subunit gene. One mutation causes skipping of exon 8, truncating the beta subunit before its M1 transmembrane domain, and abolishing surface expression of pentameric AChR. The other mutation, a 3-codon deletion (beta426delEQE) in the long cytoplasmic loop between the M3 and M4 domains, curtails but does not abolish expression. By coexpressing beta426delEQE with combinations of wild-type subunits in 293 HEK cells, we demonstrate that beta426delEQE impairs AChR assembly by disrupting a specific interaction between beta and delta subunits. Studies with related deletion and missense mutants indicate that secondary structure in this region of the beta subunit is crucial for interaction with the delta subunit. The findings imply that the mutated residues are positioned at the interface between beta and delta subunits and demonstrate contribution of this local region of the long cytoplasmic loop to AChR assembly.
Figures

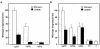
References
-
- Yu X-M, Hall ZW. Extracellular domains mediating ε subunit interactions of muscle acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1991;352:64–67. - PubMed
-
- Verrall S, Hall ZW. The N-terminal domains of the acetylcholine receptor subunits contain recognition signals for the initial steps of receptor assembly. Cell. 1992;68:23–31. - PubMed
-
- Green WN, Wanamaker CP. The role of the cystine loop in acetylcholine receptor assembly. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:20945–20953. - PubMed
-
- Gu Y, Camacho P, Gardner P, Hall ZW. Identification of two amino acid residues in the epsilon subunit that promote mammalian muscle acetylcholine receptor assembly in COS cells. Neuron. 1991;6:879–887. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

