Polycystin-1, the PKD1 gene product, is in a complex containing E-cadherin and the catenins
- PMID: 10562308
- PMCID: PMC481982
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI5111
Polycystin-1, the PKD1 gene product, is in a complex containing E-cadherin and the catenins
Abstract
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a common human genetic disease characterized by cyst formation in kidney tubules and other ductular epithelia. Cells lining the cysts have abnormalities in cell proliferation and cell polarity. The majority of ADPKD cases are caused by mutations in the PKD1 gene, which codes for polycystin-1, a large integral membrane protein of unknown function that is expressed on the plasma membrane of renal tubular epithelial cells in fetal kidneys. Because signaling from cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion complexes regulates cell proliferation and polarity, we speculated that polycystin-1 might interact with these complexes. We show here that polycystin-1 colocalized with the cell adhesion molecules E-cadherin and alpha-, beta-, and gamma-catenin. Polycystin-1 coprecipitated with these proteins and comigrated with them on sucrose density gradients, but it did not colocalize, coprecipitate, or comigrate with focal adhesion kinase, a component of the focal adhesion. We conclude that polycystin-1 is in a complex containing E-cadherin and alpha-, beta-, and gamma-catenin. These observations raise the question of whether the defects in cell proliferation and cell polarity observed in ADPKD are mediated by E-cadherin or the catenins.
Figures
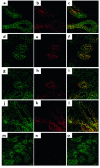
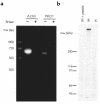
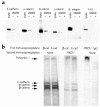

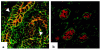
Similar articles
-
Modification of the composition of polycystin-1 multiprotein complexes by calcium and tyrosine phosphorylation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 Dec 15;1535(1):21-35. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4439(00)00079-x. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 11113628
-
Retention of membrane-localized beta-catenin in cells lacking functional polycystin-1 and tuberin.Mol Carcinog. 2002 Mar;33(3):131-6. doi: 10.1002/mc.10034. Mol Carcinog. 2002. PMID: 11870878
-
A polycystin-1 multiprotein complex is disrupted in polycystic kidney disease cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Mar;15(3):1334-46. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-05-0296. Epub 2004 Jan 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 14718571 Free PMC article.
-
Polycystin-1 interacts with E-cadherin and the catenins--clues to the pathogenesis of cyst formation in ADPKD?Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2000 Jan;15(1):1-2. doi: 10.1093/ndt/15.1.1. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2000. PMID: 10607757 Review. No abstract available.
-
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: clues to pathogenesis.Hum Mol Genet. 1999;8(10):1861-6. doi: 10.1093/hmg/8.10.1861. Hum Mol Genet. 1999. PMID: 10469838 Review.
Cited by
-
Primary cilia: the chemical antenna regulating human adipose-derived stem cell osteogenesis.PLoS One. 2013 May 17;8(5):e62554. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062554. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23690943 Free PMC article.
-
Polycystins: polymodal receptor/ion-channel cellular sensors.Pflugers Arch. 2005 Oct;451(1):264-76. doi: 10.1007/s00424-005-1431-5. Epub 2005 May 12. Pflugers Arch. 2005. PMID: 15889307 Review.
-
Inversin forms a complex with catenins and N-cadherin in polarized epithelial cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Sep;13(9):3096-106. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-04-0195. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12221118 Free PMC article.
-
The fate of the primary cilium during myofibroblast transition.Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Mar;25(5):643-57. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-07-0429. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Mol Biol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24403605 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of PKD1 gene missense mutations on polycystin-1 membrane topogenesis.Biochemistry. 2011 Jan 25;50(3):349-55. doi: 10.1021/bi101326w. Epub 2010 Dec 29. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21142036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gabow PA. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:332–342. - PubMed
-
- European Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium. The polycystic kidney disease 1 gene encodes a 14 kb transcript and lies within a duplicated region on chromosome 16. Cell. 1994;77:881–894. - PubMed
-
- American PKD1 Consortium. Analysis of the genomic sequence for the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease gene predicts the presence of a leucine-rich repeat. Hum Mol Genet. 1995;4:575–582. - PubMed
-
- International Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium. Polycystic kidney disease: the complete structure of the PKD1 gene and its protein. Cell. 1995;81:289–298. - PubMed
-
- Hughes J, et al. The polycystic kidney disease 1 gene encodes a novel protein with multiple cell recognition domains. Nat Genet. 1995;10:151–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

