Uptake and intracellular transport of acidic fibroblast growth factor: evidence for free and cytoskeleton-anchored fibroblast growth factor receptors
- PMID: 10564275
- PMCID: PMC25683
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.11.3835
Uptake and intracellular transport of acidic fibroblast growth factor: evidence for free and cytoskeleton-anchored fibroblast growth factor receptors
Abstract
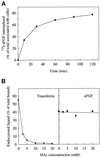
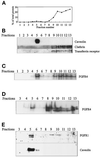
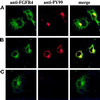
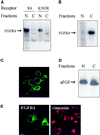
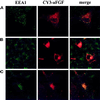
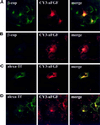
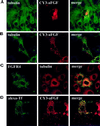
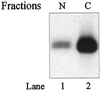
Endocytic uptake and intracellular transport of acidic FGF was studied in cells transfected with FGF receptor 4 (FGFR4). Acidification of the cytosol to block endocytic uptake from coated pits did not inhibit endocytosis of the growth factor in COS cells transfected with FGFR4, indicating that it is to a large extent taken up by an alternative endocytic pathway. Fractionation of the cells demonstrated that part of the growth factor receptor was present in a low-density, caveolin-containing fraction, but we were unable to demonstrate binding to caveolin in immunoprecipitation studies. Upon treatment of the cells with acidic FGF, the activated receptor, together with the growth factor, moved to a juxtanuclear compartment, which was identified as the recycling endosome compartment. When the cells were lysed with Triton X-100, 3-([3-chloramidopropyl]dimethylammonio)-2-hydroxy-1-propanesulfona te, or 2-octyl glucoside, almost all surface-exposed and endocytosed FGFR4 was solubilized, but only a minor fraction of the total FGFR4 in the cells was found in the soluble fraction. The data indicate that the major part of FGFR4 is anchored to detergent-insoluble structures, presumably cytoskeletal elements associated with the recycling endosome compartment.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Modulation of intracellular transport of acidic fibroblast growth factor by mutations in the cytoplasmic receptor domain.J Cell Sci. 2001 May;114(Pt 9):1677-89. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.9.1677. J Cell Sci. 2001. PMID: 11398757
-
Effect of mutation of cytoplasmic receptor domain and of genistein on transport of acidic fibroblast growth factor into cells.Oncogene. 1997 Jul 31;15(5):525-36. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201226. Oncogene. 1997. PMID: 9247306
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 is a high affinity receptor for both acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor but not for keratinocyte growth factor.J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5388-94. J Biol Chem. 1993. PMID: 7680645
-
Differential distribution of fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs) on foveal cones: FGFR-4 is an early marker of cone photoreceptors.Mol Vis. 2004 Jan 8;10:1-14. Mol Vis. 2004. PMID: 14737068
-
Characterization of a non-tyrosine kinase FGF-binding protein.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;638:195-203. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb49030.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991. PMID: 1723853 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Ebulin l Is Internalized in Cells by Both Clathrin-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms and Does Not Require Clathrin or Dynamin for Intoxication.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jan 30;13(2):102. doi: 10.3390/toxins13020102. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33573355 Free PMC article.
-
Translocation of FGF-1 and FGF-2 across vesicular membranes occurs during G1-phase by a common mechanism.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Feb;15(2):801-14. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-08-0589. Epub 2003 Dec 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 14657241 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signalling and trafficking by Src and Eps8.J Cell Sci. 2013 Jan 15;126(Pt 2):613-24. doi: 10.1242/jcs.116228. Epub 2012 Nov 30. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23203811 Free PMC article.
-
Syndecan 4 regulates FGFR1 signaling in endothelial cells by directing macropinocytosis.Sci Signal. 2012 May 8;5(223):ra36. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002495. Sci Signal. 2012. PMID: 22569333 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid rafts serve as a signaling platform for nicotinic acetylcholine receptor clustering.J Neurosci. 2006 May 3;26(18):4841-51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2807-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16672658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basilico C, Moscatelli D. The FGF family of growth factors and oncogenes. Adv Cancer Res. 1992;59:115–165. - PubMed
-
- Beck KA, Buchanan JA, Nelson WJ. Golgi membrane skeleton: identification, localization and oligomerization of a 195 kDa ankyrin isoform associated with the Golgi complex. J Cell Sci. 1997;110:1239–1249. - PubMed
-
- Bennett V. Ankyrins: adaptors between diverse plasma membrane proteins and the cytoplasm. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:8703–8706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

