The interaction and colocalization of Sam68 with the splicing-associated factor YT521-B in nuclear dots is regulated by the Src family kinase p59(fyn)
- PMID: 10564280
- PMCID: PMC25688
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.11.3909
The interaction and colocalization of Sam68 with the splicing-associated factor YT521-B in nuclear dots is regulated by the Src family kinase p59(fyn)
Abstract
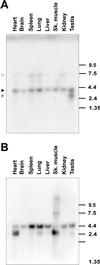
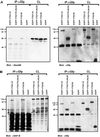
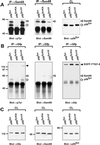
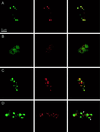
Alternative pre-mRNA splicing patterns can change an extracellular stimulus, but the signaling pathways leading to these changes are still poorly characterized. Here, we describe a tyrosine-phosphorylated nuclear protein, YT521-B, and show that it interacts with the nuclear transcriptosomal component scaffold attachment factor B, and the 68-kDa Src substrate associated during mitosis, Sam68. Northern blot analysis demonstrated ubiquitous expression, but detailed RNA in situ analysis revealed cell type specificity in the brain. YT521-B protein is localized in the nucleoplasm and concentrated in 5-20 large nuclear dots. Deletion analysis demonstrated that the formation of these dots depends on the presence of the amino-terminal glutamic acid-rich domain and the carboxyl-terminal glutamic acid/arginine-rich region. We show that the latter comprises an important protein-protein interaction domain. The Src family kinase p59(fyn)-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of Sam68 negatively regulates its association with YT521-B, and overexpression of p59(fyn) dissolves nuclear dots containing YT521-B. In vivo splicing assays demonstrated that YT521-B modulates alternative splice site selection in a concentration-dependent manner. Together, our data indicate that YT521-B and Sam68 may be part of a signal transduction pathway that influences splice site selection.
Figures







References
-
- Amara SG, Jonas V, Rosenfeld MG, Ong ES, Evans RM. Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature. 1982;298:240–244. - PubMed
-
- Baumbach WR, Horner DL, Logan JS. The growth hormone-binding protein in rat serum is an alternatively spliced form of the rat growth hormone receptor. Genes & Dev. 1989;3:1199–1205. - PubMed
-
- Beil B, Screaton G, Stamm S. Molecular cloning of htra2-beta-1 and htra2-beta-2, two human homologues of tra-2 generated by alternative splicing. DNA Cell Biol. 1997;16:679–690. - PubMed
-
- Cáceres J, Stamm S, Helfman DM, Krainer AR. Regulation of alternative splicing in vivo by overexpression of antagonistic splicing factors. Science. 1994;265:1706–1709. - PubMed
-
- Chalfant CE, Watson JE, Bisnauth LD, Kang JB, Patel N, Obeid LM, Eichler DC, Cooper DR. Insulin regulates protein kinase CbetaII expression through enhanced exon inclusion in L6 skeletal muscle cells. A novel mechanism of insulin- and insulin-like growth factor-i-induced 5′ splice site selection. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:910–916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

