d2_cluster: a validated method for clustering EST and full-length cDNAsequences
- PMID: 10568753
- PMCID: PMC310833
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.9.11.1135
d2_cluster: a validated method for clustering EST and full-length cDNAsequences
Abstract
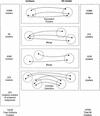
Several efforts are under way to condense single-read expressed sequence tags (ESTs) and full-length transcript data on a large scale by means of clustering or assembly. One goal of these projects is the construction of gene indices where transcripts are partitioned into index classes (or clusters) such that they are put into the same index class if and only if they represent the same gene. Accurate gene indexing facilitates gene expression studies and inexpensive and early partial gene sequence discovery through the assembly of ESTs that are derived from genes that have yet to be positionally cloned or obtained directly through genomic sequencing. We describe d2_cluster, an agglomerative algorithm for rapidly and accurately partitioning transcript databases into index classes by clustering sequences according to minimal linkage or "transitive closure" rules. We then evaluate the relative efficiency of d2_cluster with respect to other clustering tools. UniGene is chosen for comparison because of its high quality and wide acceptance. It is shown that although d2_cluster and UniGene produce results that are between 83% and 90% identical, the joining rate of d2_cluster is between 8% and 20% greater than UniGene. Finally, we present the first published rigorous evaluation of under and over clustering (in other words, of type I and type II errors) of a sequence clustering algorithm, although the existence of highly identical gene paralogs means that care must be taken in the interpretation of the type II error. Upper bounds for these d2_cluster error rates are estimated at 0.4% and 0.8%, respectively. In other words, the sensitivity and selectivity of d2_cluster are estimated to be >99.6% and 99.2%.
Figures
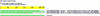


References
-
- Adams MD, Kelley JM, Gocayne JD, Dubnick M, Polymeropoulos MH, Xiao H, Merril CR, Wu A, Olde B, Moreno RF, et al. Complementary DNA sequencing: Expressed sequence tags and human genome project. Science. 1991;252:1651–1656. - PubMed
-
- Adams MD, Dubnick M, Kerlavage AR, Moreno R, Kelley JM, Utterback TR, Nagle JW, Fields C, Venter JC. Sequence identification of 2,375 human brain genes. Nature. 1992;355:632–634. - PubMed
-
- Adams MD, Kerlavage AR, Fleischmann RD, Fuldner RA, Bult CJ, Lee NH, Kirkness EF, Weinstock KG, Gocayne JD, White O, et al. Initial assessment of human gene diversity and expression patterns based upon 83 million nucleotides of cDNA sequence. Nature (Suppl.) 1995;377:3–17. - PubMed
-
- Boguski MS, Schuler GD. ESTablishing a human transcript map. Nat Genet. 1995;10:369–371. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
