Expression of recombinant enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli colonization factor antigen I by Salmonella typhimurium elicits a biphasic T helper cell response
- PMID: 10569734
- PMCID: PMC97026
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.12.6249-6256.1999
Expression of recombinant enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli colonization factor antigen I by Salmonella typhimurium elicits a biphasic T helper cell response
Abstract
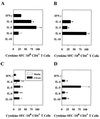
Protective immunity to enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) is antibody (Ab) dependent; however, oral immunization with purified ETEC fimbriae fails to elicit protective immunity as a consequence of antigenic alteration by the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Unless unaltered ETEC fimbriae can reach the inductive lymphoid tissues of the GI tract, immunity to ETEC cannot be induced. To produce immunity, live vectors, such as Salmonella typhimurium, can effectively target passenger antigens to the inductive lymphoid tissues of the GI tract. By convention, oral immunizations with Salmonella vectors induce CD4(+) T helper (Th) cell responses by gamma interferon (IFN-gamma)-dominated pathways both to the vector and passenger antigen, resulting in serum immunoglobulin G2a (IgG2a) and modest mucosal IgA Ab responses. In the present study, mice orally immunized with a Salmonella vector engineered to stably express ETEC colonization factor antigen I (CFA/I) showed initially elevated serum IgG1 and mucosal IgA anti-CFA/I Ab responses. As expected, mice orally immunized with an E. coli-CFA/I construct elicited poor anti-CFA/I Ab responses. In fact, the addition of cholera toxin during oral E. coli-CFA/I immunization failed to greatly enhance mucosal IgA Ab responses. Seven days after immunization with the Salmonella-CFA/I construct, cytokine-specific ELISPOT showed induction of predominant Th2-type responses in both mucosal and systemic immune compartments supporting the early IgG1 and IgA anti-CFA/I Abs. By 4 weeks, the Th cell response became Th1 cell dominant from the earlier Th2-type responses, as evidenced by increased mucosal and systemic IFN-gamma-producing T cells and a concomitant elevation of serum IgG2a Ab responses. This biphasic response offers an alternative strategy for directing Salmonella vector-induced host immunity along a Th2 cell-dependent pathway, allowing for early promotion of mucosal and systemic Abs.
Figures






References
-
- Black R E, Brown K H, Becker S, Alim A, Huq I. Longitudinal studies of infectious diseases and physical growth of children in rural Bangladesh: II. Incidence of diarrhea and association with known pathogens. Am J Epidemiol. 1982;115:315–324. - PubMed
-
- Black R E. The epidemiology of cholera and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrheal disease. In: Holmgren J, Lindberg A, Molby R, editors. Development of Vaccines and Drugs Against Diarrhea. Stockholm, Sweden: Studentlitteratur; 1986. pp. 23–32.
-
- Curtiss R, Kelly S M, Gulig P A, Nakayama K. Selective delivery of antigens by recombinant bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;146:34–49. - PubMed
-
- Curtiss R, Kelly S M, Hassan J O. Live oral avirulent Salmonellavaccines. Vet Microbiol. 1993;37:397–405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

