Activity of monosaccharide lipid A analogues in human monocytic cells as agonists or antagonists of bacterial lipopolysaccharide
- PMID: 10569739
- PMCID: PMC97031
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.12.6286-6292.1999
Activity of monosaccharide lipid A analogues in human monocytic cells as agonists or antagonists of bacterial lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
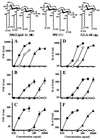
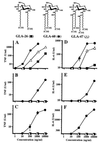
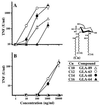
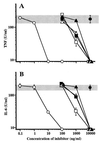
The lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) plays a central role in the production of endotoxic mediators. Different responses between human and murine macrophages to lipid A-like structures have been indicated. We investigated a series of structurally related monosaccharide lipid A analogues for their potency to activate human macrophage U937 cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells for production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 compared with their potency to activate murine macrophage RAW264.7 cells. Two of the analogues were found to have sufficient potency to activate the human cells as well as the murine cells. These analogues comprise D-glucosamine, phosphoryl groups, and acyl groups of defined carbon chain lengths (C(14) and C(12)) in a ratio of 1:1:3. This ratio of molecular constituents is proportional to that of the complete disaccharide structure of lipid A (2:2:6). Other analogues with two or four C(14) acyl groups and with three acyl groups but including a C(10) or a C(16) acyl group, which are active to murine cells, showed no LPS-agonistic activity, but did show LPS-antagonistic activity, to human cells. An LPS-antagonistic analogue in the murine cells also showed antagonistic activity in human cells. These results reveal that lipid A analogues recognized as being LPS agonists by human macrophages have common structural features in monosaccharide and disaccharide structures which are more strict than those required for recognition by murine macrophages and that broad lipid A-like structures are recognized as being LPS antagonists by human cells but are recognized by murine cells as being either LPS agonists or antagonists.
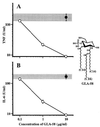
Figures

References
-
- Aarden L A, de Groot E R, Shaap O L, Lansdorp P M. Production of hybridoma growth factor by human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987;7:1411–1416. - PubMed
-
- Boyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood: isolation of mononuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Investig. 1968;21:77–89. - PubMed
-
- Brandenburg K, Mayer H, Koch M H J, Weckesser J, Rietschel E T, Seydel U. Influence of the supramolecular structure of free lipid A on its biological activity. Eur J Biochem. 1993;218:555–563. - PubMed
-
- Ding A, Porteu F, Sanchez E, Nathan C F. Shared actions of endotoxin and Taxol on TNF receptors and TNF release. Science. 1990;248:370–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

