Antibody C219 recognizes an alpha-helical epitope on P-glycoprotein
- PMID: 10570132
- PMCID: PMC24124
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.24.13679
Antibody C219 recognizes an alpha-helical epitope on P-glycoprotein
Abstract
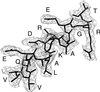
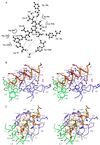
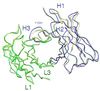
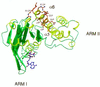
The ABC transporter, P-glycoprotein, is an integral membrane protein that mediates the ATP-driven efflux of drugs from multidrug-resistant cancer and HIV-infected cells. Anti-P-glycoprotein antibody C219 binds to both of the ATP-binding regions of P-glycoprotein and has been shown to inhibit its ATPase activity and drug binding capacity. C219 has been widely used in a clinical setting as a tumor marker, but recent observations of cross-reactivity with other proteins, including the c-erbB2 protein in breast cancer cells, impose potential limitations in detecting P-glycoprotein. We have determined the crystal structure at a resolution of 2.4 A of the variable fragment of C219 in complex with an epitope peptide derived from the nucleotide binding domain of P-glycoprotein. The 14-residue peptide adopts an amphipathic alpha-helical conformation, a secondary structure not previously observed in structures of antibody-peptide complexes. Together with available biochemical data, the crystal structure of the C219-peptide complex indicates the molecular basis of the cross-reactivity of C219 with non-multidrug resistance-associated proteins. Alignment of the C219 epitope with the recent crystal structure of the ATP-binding subunit of histidine permease suggests a structural basis for the inhibition of the ATP and drug binding capacity of P-glycoprotein by C219. The results provide a rationale for the development of C219 mutants with improved specificity and affinity that could be useful in antibody-based P-glycoprotein detection and therapy in multidrug resistant cancers.
Figures


References
-
- Kartner N, Shales M, Riordan J R, Ling V. Cancer Res. 1983;43:4413–4419. - PubMed
-
- Higgins C F. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:67–113. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg M F, Callaghan R, Ford R C, Higgins C F. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:10685–10694. - PubMed
-
- Kartner N, Evernden-Porelle D, Bradley G, Ling V. Nature (London) 1985;316:820–823. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

