Dynamin-dependent endocytosis of ionotropic glutamate receptors
- PMID: 10570207
- PMCID: PMC24199
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.24.14112
Dynamin-dependent endocytosis of ionotropic glutamate receptors
Abstract
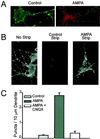
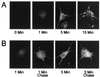
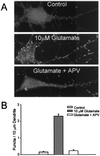
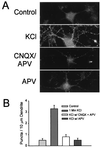
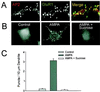
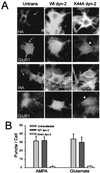
Little is known about the mechanisms that regulate the number of ionotropic glutamate receptors present at excitatory synapses. Herein, we show that GluR1-containing alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors (AMPARs) are removed from the postsynaptic plasma membrane of cultured hippocampal neurons by rapid, ligand-induced endocytosis. Although endocytosis of AMPARs can be induced by high concentrations of AMPA without concomitant activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors (NMDARs), NMDAR activation is required for detectable endocytosis induced by synaptically released glutamate. Activated AMPARs colocalize with AP2, a marker of endocytic coated pits, and endocytosis of AMPARs is blocked by biochemical inhibition of clathrin-coated pit function or overexpression of a dominant-negative mutant form of dynamin. These results establish that ionotropic receptors are regulated by dynamin-dependent endocytosis and suggest an important role of endocytic membrane trafficking in the postsynaptic modulation of neurotransmission.
Figures
References
-
- Hollmann M, Heinemann S. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:31–108. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien R J, Lau L F, Huganir R L. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1998;8:364–369. - PubMed
-
- Seeburg P H. Trends Neurosci. 1993;16:359–365. - PubMed
-
- Gomperts S N, Rao A, Craig A M, Malenka R C, Nicoll R A. Neuron. 1998;21:1443–1451. - PubMed
-
- Malenka R C, Nicoll R A. Neuron. 1997;19:473–476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

