Unusual structure of the attB site of the site-specific recombination system of Lactobacillus delbrueckii bacteriophage mv4
- PMID: 10572145
- PMCID: PMC103704
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.23.7385-7389.1999
Unusual structure of the attB site of the site-specific recombination system of Lactobacillus delbrueckii bacteriophage mv4
Abstract
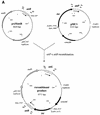
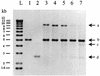
The temperate phage mv4 integrates its genome into the chromosome of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus by site-specific recombination within the 3' end of a tRNA(Ser) gene. Recombination is catalyzed by the phage-encoded integrase and occurs between the phage attP site and the bacterial attB site. In this study, we show that the mv4 integrase functions in vivo in Escherichia coli and we characterize the bacterial attB site with a site-specific recombination test involving compatible plasmids carrying the recombination sites. The importance of particular nucleotides within the attB sequence was determined by site-directed mutagenesis. The structure of the attB site was found to be simple but rather unusual. A 16-bp DNA fragment was sufficient for function. Unlike most genetic elements that integrate their DNA into tRNA genes, none of the dyad symmetry elements of the tRNA(Ser) gene were present within the minimal attB site. No inverted repeats were detected within this site either, in contrast to the lambda site-specific recombination model.
Figures


References
-
- Abremski K, Hoess R. Evidence for a second conserved arginine residue in the integrase family of recombination proteins. Protein Eng. 1992;5:87–91. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez M A, Herrero M, Suarez J E. The site-specific recombination system of the Lactobacillus species bacteriophage A2 integrates in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Virology. 1998;250:185–193. - PubMed
-
- Auvray F, Coddeville M, Espagno G, Ritzenthaler P. Integrative recombination of Lactobacillus delbrueckii bacteriophage mv4: functional analysis of the reaction and structure of the attP site. Mol Gen Genet. 1999;262:355–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

