Actin filaments and the opposing actions of CaM kinase II and calcineurin in regulating alpha7-containing nicotinic receptors on chick ciliary ganglion neurons
- PMID: 10575025
- PMCID: PMC6782428
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-23-10280.1999
Actin filaments and the opposing actions of CaM kinase II and calcineurin in regulating alpha7-containing nicotinic receptors on chick ciliary ganglion neurons
Abstract
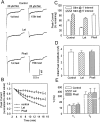
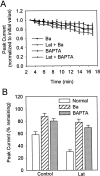
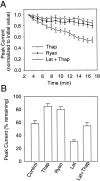
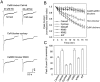
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors containing alpha7 subunits have a high relative permeability to calcium and influence numerous calcium-dependent cellular events. On chick ciliary ganglion neurons the receptors are concentrated on somatic spines containing actin filaments. Using conventional whole-cell patch-clamp recording from dissociated ciliary ganglion neurons, we show that responses from alpha7-containing receptors undergo substantial rundown when the receptors are repeatedly challenged with nicotine. Stabilization of actin filaments with phalloidin partially prevents the rundown, whereas collapse of actin filaments with latrunculin A exacerbates it. The rundown depends on calcium influx through the receptors because it requires receptor activation and can be prevented by replacing extracellular calcium with barium or by intracellular dialysis with BAPTA. Thapsigargin and ryanodine each inhibit the rundown, demonstrating further a requirement for calcium release from internal stores. Blockade of calmodulin by calmidazolium or blockade of CaM kinase II with either KN93 or autocamtide-2-related inhibitory peptide each prevents the rundown; blockade of the phosphatase calcineurin with either cyclosporin A or deltamethrin increases the rundown. The results indicate a balance of calcium-dependent kinase and phosphatase activities in regulating the function of alpha7-containing receptors. Manifestation of the rundown depends in part on the loss of intracellular components via dialysis because little rundown is seen if perforated patch-clamp recording is used to monitor receptor responses even in latrunculin A-treated cells. A membrane-permeable calcineurin inhibitor, however, still decreases the nicotinic response in a calcium-dependent manner, confirming that calcium-dependent phosphoregulation of alpha7-containing receptors occurs in the intact cell.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Extracellular calcium regulates responses of both alpha3- and alpha7-containing nicotinic receptors on chick ciliary ganglion neurons.J Neurophysiol. 1999 Sep;82(3):1124-32. doi: 10.1152/jn.1999.82.3.1124. J Neurophysiol. 1999. PMID: 10482732
-
Reversible inhibition of GABAA receptors by alpha7-containing nicotinic receptors on the vertebrate postsynaptic neurons.J Physiol. 2007 Mar 15;579(Pt 3):753-63. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.124578. Epub 2007 Jan 4. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17204496 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptically driven calcium transients via nicotinic receptors on somatic spines.J Neurosci. 2001 Feb 1;21(3):771-81. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-03-00771.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11157063 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoskeletal links of neuronal acetylcholine receptors containing alpha 7 subunits.J Neurosci. 2000 Jun 1;20(11):4021-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-11-04021.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10818137 Free PMC article.
-
Role of endogenous nicotinic signaling in guiding neuronal development.Biochem Pharmacol. 2007 Oct 15;74(8):1112-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.05.022. Epub 2007 Jun 2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17603025 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Calcineurin-Dependent Homeostatic Response of C. elegans Muscle Cells upon Prolonged Activation of Acetylcholine Receptors.Cells. 2023 Sep 3;12(17):2201. doi: 10.3390/cells12172201. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37681933 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane lipid rafts are necessary for the maintenance of the (alpha)7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in somatic spines of ciliary neurons.J Neurosci. 2001 Jan 15;21(2):504-12. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-02-00504.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11160430 Free PMC article.
-
Clustering of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: from the neuromuscular junction to interneuronal synapses.Mol Neurobiol. 2002 Feb;25(1):79-112. doi: 10.1385/MN:25:1:079. Mol Neurobiol. 2002. PMID: 11890459 Review.
-
Rapid activity-driven SNARE-dependent trafficking of nicotinic receptors on somatic spines.J Neurosci. 2005 Feb 2;25(5):1159-68. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3953-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15689552 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are negatively regulated by tyrosine phosphorylation and Src-family kinases.J Neurosci. 2005 Oct 26;25(43):9836-49. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3497-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16251431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anand R, Peng X, Lindstrom J. Homomeric and native α7 acetylcholine receptors exhibit remarkably similar but non-identical pharmacological properties, suggesting that the native receptor is a heteromeric protein complex. FEBS Lett. 1993;327:241–246. - PubMed
-
- Bonfante-Cabarcas R, Swanson KL, Alkondon M, Albuquerque EX. Diversity of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat hippocampal neurons. IV. Regulation by external Ca++ of α-bungarotoxin-sensitive receptor function and of rectification induced by internal Mg++. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;277:432–444. - PubMed
-
- Choi DW. Excitotoxic cell death. J Neurobiol. 1992;23:1261–1276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
