Effects of chronic antidepressant treatments on serotonin transporter function, density, and mRNA level
- PMID: 10575045
- PMCID: PMC6782424
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-23-10494.1999
Effects of chronic antidepressant treatments on serotonin transporter function, density, and mRNA level
Abstract
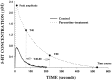
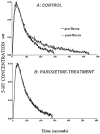
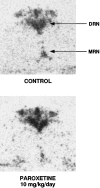
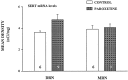
To investigate functional changes in the brain serotonin transporter (SERT) after chronic antidepressant treatment, several techniques were used to assess SERT activity, density, or its mRNA content. Rats were treated by osmotic minipump for 21 d with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) paroxetine or sertraline, the selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor desipramine (DMI), or the monoamine oxidase inhibitor phenelzine. High-speed in vivo electrochemical recordings were used to assess the ability of the SSRI fluvoxamine to modulate the clearance of locally applied serotonin in the CA3 region of hippocampus in drug- or vehicle-treated rats. Fluvoxamine decreased the clearance of serotonin in rats treated with vehicle, DMI, or phenelzine but had no effect on the clearance of serotonin in SSRI-treated rats. SERT density in the CA3 region of the hippocampus of the same rats, assessed by quantitative autoradiography with tritiated cyanoimipramine ([(3)H]CN-IMI), was decreased by 80-90% in SSRI-treated rats but not in those treated with phenelzine or DMI. The serotonin content of the hippocampus was unaffected by paroxetine or sertraline treatment, ruling out neurotoxicity as a possible explanation for the SSRI-induced decrease in SERT binding and alteration in 5-HT clearance. Levels of mRNA for the SERT in the raphe nucleus were also unaltered by chronic paroxetine treatment. Based on these results, it appears that the SERT is downregulated by chronic administration of SSRIs but not other types of antidepressants; furthermore, the downregulation is not caused by decreases in SERT gene expression.
Figures



References
-
- Auerbach SB, Hjorth S. Effect of chronic administration of the selective serotonin (5-HT) uptake inhibitors citalopram on extracellular 5-HT and apparent autoreceptor sensitivity in rat forebrain in vivo. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1995;352:597–606. - PubMed
-
- Blakely RD, Ramamoorthy S, Qian Y, Schroeter S, Bradley CC. Regulation of antidepressant-sensitive serotonin transporters. In: Reith MEA, editor. Neurotransmitter transporters. Structure, function and regulation. Humana; Totowa, NJ: 1997. pp. 29–72.
-
- Brunello N, Riva M, Volterra A, Racagni G. Effect of some tricyclic and nontricyclic antidepressants on [3H]imipramine binding and serotonin uptake in rat cerebral cortex after prolonged treatment. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1987;1:327–333. - PubMed
-
- Burnet PWJ, Michelson D, Smith MA, Gold PW, Sternberg EM. The effect of chronic imipramine administration on the densities of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptor and the abundancies of 5-HT receptor and transporter mRNA in the cortex, hippocampus and dorsal raphe of tree strain of rats. Brain Res. 1994;638:311–324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
