Cortical spreading depression in the gyrencephalic feline brain studied by magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 10577057
- PMCID: PMC2269513
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0415m.x
Cortical spreading depression in the gyrencephalic feline brain studied by magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
1.Time-lapse diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI) was used to detect and characterize complex waves of cortical spreading depression (CSD) evoked with KCL placed upon the suprasylvian gyrus of anaesthetized cats. 2. The time-lapse representations successfully demonstrated primary CSD waves that propagated with elliptical wavefronts selectively over the ipsilateral cerebral hemispheres with a velocity of 3.8 +/- 0.70 mm min(-1) (mean +/- S.E.M. of 5 experiments). 3. In contrast, the succeeding secondary waves often remained within the originating gyrus, were slower (velocity 2.0 +/- 0.18 mm min(-1), more fragmented and varied in number. 4. Computed traces of the apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) showed negative deflections followed by monotonic decays (amplitudes: primary wave, -19.9 +/- 2.8%; subsequent waves, -13.6 +/- 1.9% duration at half-maximal decay, 150-200 s) when determined from regions of interest (ROIs) through which both primary and succeeding CSD waves propagated. 5. The passage of both the primary and the succeeding waves often correlated with transient DC potential deflections recorded from the suprasylvian gyrus. 6. The detailed waveforms of the ADC and the T2*-weighted (blood oxygenation level-dependent: BOLD) traces showed a clear reciprocal correlation. These imaging features that reflect disturbances in cellular water balance agree closely with BOLD measurements that followed the propagation velocities of the first and subsequent CSD events. They also provide a close physiological correlate for clinical observations of cortical blood flow disturbances associated with human migraine.
Figures
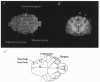


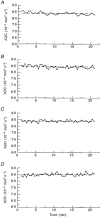

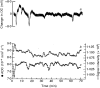
References
-
- Back T, Kohno K, Hossmann KA. Cortical negative DC deflections following middle cerebral artery occlusion and KCl-induced spreading depression: effect on blood flow, tissue oxygenation, and electroencephalogram. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 1994;14:12–19. - PubMed
-
- Bures J, Buresova O, Krivanek J. The meaning and significance of Leao's spreading depression. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciencias. 1984;56:385–400. - PubMed
-
- Chopp M. Editorial comment: spreading depression. Cephalagia. 1996;16:77. - PubMed
-
- Cutrer FM, Sorenson AG, Weisskoff RM, Ostergaard L, Sanchez Del Rio M, Lee EJ, Rosen EJ, Moskowitz MA. Perfusion-weighted imaging defects during spontaneous migrainous aura. Annals of Neurology. 1988;43:25–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

