Digenic junctional epidermolysis bullosa: mutations in COL17A1 and LAMB3 genes
- PMID: 10577906
- PMCID: PMC1288363
- DOI: 10.1086/302672
Digenic junctional epidermolysis bullosa: mutations in COL17A1 and LAMB3 genes
Abstract
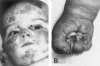
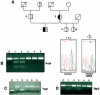
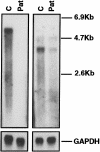
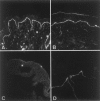
Junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB), a genetically heterogeneous group of blistering skin diseases, can be caused by mutations in the genes encoding laminin 5 or collagen XVII, which are components of the hemidesmosome-anchoring filament complex in the skin. Here, a family with severe nonlethal JEB and with mutations in genes for both proteins was identified. The index patient was compound heterozygous for the COL17A1 mutations L855X and R1226X and was heterozygous for the LAMB3 mutation R635X. As a consequence, two functionally related proteins were affected. Absence of collagen XVII and attenuated laminin 5 expression resulted in rudimentary hemidesmosome structure and separation of the epidermis from the basement membrane, with severe skin blistering as the clinical manifestation. In contrast, single heterozygotes carrying either (1) one or the other of the COL17A1 null alleles or (2) a double heterozygote for a COL17A1 and a LAMB3 null allele did not have a pathological skin phenotype. These observations indicate that the known allelic heterogeneity in JEB is further complicated by interactions between unlinked mutations. They also demonstrate that identification of one mutation in one gene is not sufficient for determination of the genetic basis of JEB in a given family.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Laminin 332 in junctional epidermolysis bullosa.Cell Adh Migr. 2013 Jan-Feb;7(1):135-41. doi: 10.4161/cam.22418. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Cell Adh Migr. 2013. PMID: 23076207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Junctional epidermolysis bullosa in the Middle East: clinical and genetic studies in a series of consanguineous families.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002 Apr;46(4):510-6. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2002.119673. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002. PMID: 11907499
-
Alterations in the microenvironment of junctional epidermolysis bullosa keratinocytes: A gene expression study.Matrix Biol. 2025 Feb;135:12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2024.11.005. Epub 2024 Nov 28. Matrix Biol. 2025. PMID: 39615637
-
Identification of a Novel COL17A1 Compound Heterozygous Mutation in a Chinese Girl with Non-Herlitz Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa.Curr Med Sci. 2020 Aug;40(4):795-800. doi: 10.1007/s11596-020-2234-9. Epub 2020 Aug 29. Curr Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32862392
-
Type XVII collagen gene mutations in junctional epidermolysis bullosa and prospects for gene therapy.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003 Jan;28(1):53-60. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2230.2003.01192.x. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003. PMID: 12558632 Review.
Cited by
-
Laminin 332 in junctional epidermolysis bullosa.Cell Adh Migr. 2013 Jan-Feb;7(1):135-41. doi: 10.4161/cam.22418. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Cell Adh Migr. 2013. PMID: 23076207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bilineal disease and trans-heterozygotes in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Feb;68(2):355-63. doi: 10.1086/318188. Epub 2001 Jan 10. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11156533 Free PMC article.
-
HMCN1 variants aggravate epidermolysis bullosa simplex phenotype.J Exp Med. 2025 May 5;222(5):e20240827. doi: 10.1084/jem.20240827. Epub 2025 Feb 20. J Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 39976600 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of likely pathogenic and known variants in TSPEAR, LAMB3, BCOR, and WNT10A in four Turkish families with tooth agenesis.Hum Genet. 2018 Sep;137(9):689-703. doi: 10.1007/s00439-018-1907-y. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Hum Genet. 2018. PMID: 30046887 Free PMC article.
-
Whole exome sequencing study of adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma reveals the mutational characteristics of recurrent cases.J Neurooncol. 2025 Oct;175(1):35-46. doi: 10.1007/s11060-025-05061-6. Epub 2025 Jul 29. J Neurooncol. 2025. PMID: 40731085 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for JEB Herlitz [MIM 226700] and GABEB [MIM 226650])
References
-
- Aberdam D, Aguzzi A, Baudoin C, Galliano M-F, Ortonne J-P, Meneguzzi G (1994) Developmental expression of nicein adhesion protein (laminin-5) subunits suggests multiple morphogenic roles. Cell Adhes Commun 2:115–129 - PubMed
-
- Aumailley M, Rousselle P (1999) Laminins of the dermo-epidermal junction. Matrix Biol 18:19–28 - PubMed
-
- Bruckner-Tuderman L. Epidermolysis bullosa. In: Royce P, Steinmann B (eds) Extracellular matrix and its heritable disorders of connective tissue. Wiley-Liss, New York (in press)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

