Activation of Ca(2+)-dependent K(+) channels contributes to rhythmic firing of action potentials in mouse pancreatic beta cells
- PMID: 10578013
- PMCID: PMC2230648
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.114.6.759
Activation of Ca(2+)-dependent K(+) channels contributes to rhythmic firing of action potentials in mouse pancreatic beta cells
Abstract
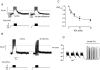
We have applied the perforated patch whole-cell technique to beta cells within intact pancreatic islets to identify the current underlying the glucose-induced rhythmic firing of action potentials. Trains of depolarizations (to simulate glucose-induced electrical activity) resulted in the gradual (time constant: 2.3 s) development of a small (<0.8 nS) K(+) conductance. The current was dependent on Ca(2+) influx but unaffected by apamin and charybdotoxin, two blockers of Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels, and was insensitive to tolbutamide (a blocker of ATP-regulated K(+) channels) but partially (>60%) blocked by high (10-20 mM) concentrations of tetraethylammonium. Upon cessation of electrical stimulation, the current deactivated exponentially with a time constant of 6.5 s. This is similar to the interval between two successive bursts of action potentials. We propose that this Ca(2+)-activated K(+) current plays an important role in the generation of oscillatory electrical activity in the beta cell.
Figures

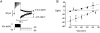
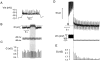
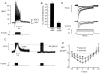

References
-
- Ämmälä C., Bokvist K., Larsson O., Berggren P.O., Rorsman P. Demonstration of a novel apamin-insensitive calcium-activated K+ channel in mouse pancreatic B cells Pflügers Arch. 422 1993. 443 448b - PubMed
-
- Ämmälä C., Larsson O., Berggren P.O., Bokvist K., Juntti-Berggren L., Kindmark H., Rorsman P. Inositol triphosphate–dependent periodic activation of a Ca2+-activated K+ conductance in glucose-stimulated pancreatic β-cells. Nature. 1991;353:849–852. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft F.M., Rorsman P. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic β-cell. Prog. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989;54:87–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

