Diffuse bipolar cells provide input to OFF parasol ganglion cells in the macaque retina
- PMID: 10578099
- PMCID: PMC3347706
- DOI: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(20000103)416:1<6::aid-cne2>3.0.co;2-x
Diffuse bipolar cells provide input to OFF parasol ganglion cells in the macaque retina
Abstract
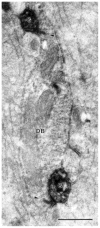
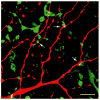
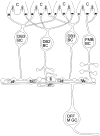
Parasol retinal ganglion cells are more sensitive to luminance contrast and respond more transiently at all levels of adaptation than midget ganglion cells. This may be due, in part, to differences between bipolar cells that provide their input, and the goal of these experiments was to study these differences. Midget bipolar cells are known to be presynaptic to midget ganglion cells. To identify the bipolar cells presynaptic to parasol cells, these ganglion cells were intracellularly injected with Neurobiotin, cone bipolar cells were immunolabeled, and the double-labeled material was analyzed. In the electron microscope, we found that DB3 diffuse bipolar cells labeled by using antiserum to calbindin D-28k were presynaptic to OFF parasol cells. In the confocal microscope, DB3 bipolars costratified with OFF parasol cell dendrites and made significantly more appositions with them than expected due to chance. Flat midget bipolar cells were labeled with antiserum to recoverin. Although they made a few appositions with parasol cells, the number was no greater than would be expected when two sets of processes have overlapping distributions in the inner plexiform layer. DB2 diffuse bipolar cells were labeled with antibodies to excitatory amino acid transporter 2, and they also made appositions with OFF parasol cells. These results suggest that DB2 bipolar cells are also presynaptic to OFF parasol ganglion cells, but midget bipolar cells are not. We estimate that midperipheral OFF parasol cells receive approximately 500 synapses from 50 DB3 bipolar cells that, in turn, receive input from 250 cones.
Copyright 2000 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Synaptic input to OFF parasol ganglion cells in macaque retina.J Comp Neurol. 2006 Sep 1;498(1):46-57. doi: 10.1002/cne.21040. J Comp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16856174 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic input to an ON parasol ganglion cell in the macaque retina: a serial section analysis.Vis Neurosci. 2002 May-Jun;19(3):299-305. doi: 10.1017/s0952523802192078. Vis Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12392179 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic connections of DB3 diffuse bipolar cell axons in macaque retina.J Comp Neurol. 2000 Jan 3;416(1):19-29. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(20000103)416:1<19::aid-cne3>3.0.co;2-h. J Comp Neurol. 2000. PMID: 10578100 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct synaptic mechanisms create parallel S-ON and S-OFF color opponent pathways in the primate retina.Vis Neurosci. 2014 Mar;31(2):139-51. doi: 10.1017/S0952523813000230. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Vis Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 23895762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distribution of GABA and glycine receptors on bipolar and ganglion cells in the mammalian retina.Microsc Res Tech. 2000 Jul 15;50(2):130-40. doi: 10.1002/1097-0029(20000715)50:2<130::AID-JEMT5>3.0.CO;2-I. Microsc Res Tech. 2000. PMID: 10891877 Review.
Cited by
-
Wiring patterns in the mouse retina: collecting evidence across the connectome, physiology and light microscopy.J Physiol. 2014 Nov 15;592(22):4809-23. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.277228. Epub 2014 Aug 28. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25172948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wide-field ganglion cells in macaque retinas.Vis Neurosci. 2005 Jul-Aug;22(4):383-93. doi: 10.1017/S095252380522401X. Vis Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16212697 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical identification and synaptic inputs to the diffuse bipolar cell type DB1 in macaque retina.J Comp Neurol. 2011 Dec 15;519(18):3640-56. doi: 10.1002/cne.22756. J Comp Neurol. 2011. PMID: 22006647 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic input to OFF parasol ganglion cells in macaque retina.J Comp Neurol. 2006 Sep 1;498(1):46-57. doi: 10.1002/cne.21040. J Comp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16856174 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic input to an ON parasol ganglion cell in the macaque retina: a serial section analysis.Vis Neurosci. 2002 May-Jun;19(3):299-305. doi: 10.1017/s0952523802192078. Vis Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12392179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boycott BB, Wässle H. Morphological classification of bipolar cells of the primate retina. Eur J Neurosci. 1991;3:1069–1088. - PubMed
-
- Calkins DJ, Schein SJ, Tsukamoto Y, Sterling P. M and L cones in macaque fovea connect to midget ganglion cells by different numbers of excitatory synapses. Nature. 1994;371:70–72. - PubMed
-
- Calkins D, Schein S, Sterling P. Cone inputs to three types of non-midget ganglion cell in macaque fovea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1995;36:S4.
-
- Calkins DJ. Synaptic organization of cone pathways in the primate retina. In: Gegenfurtner K, Sharpe L, editors. Color vision: from genes to perception. New York: Cambridge University Press; 1999.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

