Identification of the G-protein-coupled ORL1 receptor in the mouse spinal cord by [35S]-GTPgammaS binding and immunohistochemistry
- PMID: 10578145
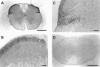
- PMCID: PMC1571752
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702907
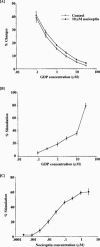
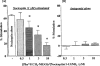
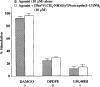
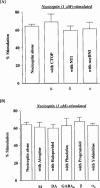
Identification of the G-protein-coupled ORL1 receptor in the mouse spinal cord by [35S]-GTPgammaS binding and immunohistochemistry
Abstract
1 Although the ORL1 receptor is clearly located within the spinal cord, the functional signalling mechanism of the ORL1 receptor in the spinal cord has not been clearly documented. The present study was then to investigate the guanine nucleotide binding protein (G-protein) activation mediated through by the ORL1 receptor in the mouse spinal cord, measuring the modulation of guanosine-5'-o-(3-[35S]-thio) triphosphate ([35S]-GTPgammaS) binding by the putative endogenous ligand nociceptin, also referred as orphanin FQ. We also studied the anatomical distribution of nociceptin-like immunoreactivity and nociceptin-stimulated [35S]-GTPgammaS autoradiography in the spinal cord. 2 Immunohistochemical staining of mouse spinal cord sections revealed a dense plexus of nociceptin-like immunoreactive fibres in the superficial layers of the dorsal horn throughout the entire length of the spinal cord. In addition, networks of fibres were seen projecting from the lateral border of the dorsal horn to the lateral grey matter and around the central canal. 3 In vitro [35S]-GTPgammaS autoradiography showed high levels of nociceptin-stimulated [35S]-GTPgammaS binding in the superficial layers of the mouse dorsal horn and around the central canal, corresponding to the areas where nociceptin-like immunoreactive fibres were concentrated. 4 In [35S]-GTPgammaS membrane assay, nociceptin increased [35S]-GTPgammaS binding of mouse spinal cord membranes in a concentration-dependent and saturable manner, affording maximal stimulation of 64.1+/-2.4%. This effect was markedly inhibited by the specific ORL1 receptor antagonist [Phe1Psi (CH2-NH) Gly2] nociceptin (1 - 13) NH2. None of the mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid and other G-protein-coupled receptor antagonists had a significant effect on basal or nociceptin-stimulated [35S]-GTPgammaS binding. 5 These findings suggest that nociceptin-containing fibres terminate in the superficial layers of the dorsal horn and the central canal and that nociceptin released in these areas may selectively stimulate the ORL1 receptor to activate G-protein. Furthermore, the unique pattern of G-protein activation in the present study provide additional evidence that nociceptin is distinct from the mu-, delta- or kappa-opioid system.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anatomical distribution of mu, delta, and kappa opioid- and nociceptin/orphanin FQ-stimulated [35S]guanylyl-5'-O-(gamma-thio)-triphosphate binding in guinea pig brain.J Comp Neurol. 1997 Oct 6;386(4):562-72. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19971006)386:4<562::aid-cne4>3.0.co;2-0. J Comp Neurol. 1997. PMID: 9378852
-
In vitro inhibitory effects of J-113397 on nociceptin/orphanin FQ-stimulated.Neuroreport. 2001 Jun 13;12(8):1757-61. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200106130-00048. Neuroreport. 2001. PMID: 11409754
-
Nociceptin (orphanin FQ): high-affinity and high-capacity binding site coupled to low-potency stimulation of guanylyl-5'-O-(gamma-thio)-triphosphate binding in rat brain membranes.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998 Aug;286(2):896-902. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998. PMID: 9694948
-
[Effects of newly isolated opioid peptides on G-protein activation: usefulness of [35S] GTP gamma S binding study and its practical application].Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1998 Aug;18(4):107-16. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1998. PMID: 9866825 Review. Japanese.
-
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ: role in nociceptive information processing.Prog Neurobiol. 1999 Apr;57(5):527-35. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(98)00067-7. Prog Neurobiol. 1999. PMID: 10215100 Review.
Cited by
-
[Dmt1]N/OFQ(1-13)-NH2: a potent nociceptin/orphanin FQ and opioid receptor universal agonist.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Jan;168(1):151-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02115.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 22827708 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and ex vivo effects of a selective nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) peptide receptor antagonist, CompB, on specific binding of [3H]N/OFQ and [35S]GTPgammaS in rat brain and spinal cord.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Aug;139(8):1462-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705371. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12922933 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic studies of novel inhibitors of endomorphin degrading enzymes.Med Chem Res. 2012 Jul;21(7):1445-1450. doi: 10.1007/s00044-011-9666-5. Epub 2011 May 20. Med Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22707871 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of kappa opioid receptor mediated, dynorphin-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding in mouse striatum for the evaluation of selective KOR ligands in an endogenous setting.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Dec;99:131-41. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.07.001. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 26160155 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Based SAR in the Design of Selective or Bifunctional Nociceptin (NOP) Receptor Agonists.AAPS J. 2021 May 11;23(3):68. doi: 10.1208/s12248-021-00589-7. AAPS J. 2021. PMID: 33974173
References
-
- ANTON B., FEIN J., TO T., LI X., SILBERSTEIN L., EVANS C.J. Immunohistochemical colocalization of ORL-1 in the central nervous system of the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1996;368:229–251. - PubMed
-
- BUNZOW J.R., SAEZ C., MORTRUD M., BOUVIER C., WILLIAMS J.T., LOW M., GRANDY D.K. Molecular cloning and tissue distribution of a putative member of the rat opioid receptor type. FEBS Lett. 1994;347:284–288. - PubMed
-
- CERVERO F., IGGO A., OGAWA H. Nociceptor-driven dorsal horn neurones in the lumbar spinal cord of the cat. Pain. 1976;2:5–14. - PubMed
-
- CHRISTENSEN B.N., PERL E.R. Spinal neurons specifically excited by noxious or thermal stimuli: Marginal zones of the dorsal horn. J. Neurophysiol. 1970;33:293–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

