Characterization of the in vitro effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) on identified neurones of the rat dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (DMV)
- PMID: 10578146
- PMCID: PMC1571753
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702908
Characterization of the in vitro effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) on identified neurones of the rat dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (DMV)
Abstract
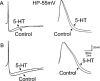
1 Whole cell patch clamp techniques were used on thin brainstem slices to investigate the effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) on gastrointestinal-projecting dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (DMV) neurones. Neurones were identified as projecting to the stomach (n=122) or intestine (n=84) if they contained the fluorescent tracer Dil after it had been applied to the gastric fundus, corpus or antrum/pylorus or to the duodenum or caecum. 2 A higher proportion of intestinal neurones (69%) than gastric neurones (47%) responded to 5-HT with a concentration-dependent inward current which was antagonized fully by the 5-HT2A receptor antagonist ketanserin (1 microM). 3 Stimulation of the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) induced inhibitory synaptic currents that were reduced in amplitude by application of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-OHDPAT (1 microM) or the 5-HT1A/1B receptor agonist TFMPP (1 microM) in 61% and 52% of gastric- and intestinal-projecting neurones, respectively. 5-HT also significantly reduced the frequency but not the amplitude of spontaneous inhibitory currents. 4 These data show that 5-HT excites directly a larger proportion of intestinal projecting neurones than gastric-projecting neurones, as well as inhibiting synaptic transmission from the NTS to the DMV. These data imply that the response to DMV neurones to 5-HT may be determined and classified by their specific projections.
Figures
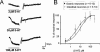


References
-
- ALTSCHULER S.M., BAO X., BIEGER D., HOPKINS D.A., MISELIS R.R. Viscerotopic representation of the upper alimentrary tract in the rat: sensory ganglia and nuclei of the solitary and spinal trigeminal tracts. J. Comp. Neurol. 1989;283:248–268. - PubMed
-
- ALTSCHULER S.M., FERENCI D.A., LYNN R.B., MISELIS R.R. Representation of the cecum in the lateral dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve and commissural subnucleus of the nucleus tractus solitarii in rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1991;304:261–274. - PubMed
-
- ANDRADE R., CHAPUT Y. 5-hydroxytryptamine 4-like receptors mediate the slow excitatory response to serotonin in the rat hippocampus. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1991a;257:930–937. - PubMed
-
- ANDRADE R., CHAPUT Y.The electrophysiology of serotonin receptor subtypes Sertonin receptor subtypes 1991bWilly: Liss; 103–124.In: Perout Ka, SJ (ed.)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

