Cell cycle-regulated attachment of the ubiquitin-related protein SUMO to the yeast septins
- PMID: 10579719
- PMCID: PMC2169351
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.147.5.981
Cell cycle-regulated attachment of the ubiquitin-related protein SUMO to the yeast septins
Abstract
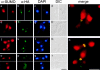
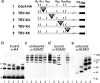
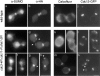
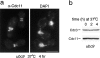
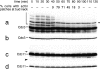
SUMO is a ubiquitin-related protein that functions as a posttranslational modification on other proteins. SUMO conjugation is essential for viability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and is required for entry into mitosis. We have found that SUMO is attached to the septins Cdc3, Cdc11, and Shs1/Sep7 specifically during mitosis, with conjugates appearing shortly before anaphase onset and disappearing abruptly at cytokinesis. Septins are components of a belt of 10-nm filaments encircling the yeast bud neck. Intriguingly, only septins on the mother cell side of the bud neck are sumoylated. We have identified four major SUMO attachment-site lysine residues in Cdc3, one in Cdc11, and two in Shs1, all within the consensus sequence (IVL)KX(ED). Mutating these sites eliminated the vast majority of bud neck-associated SUMO, as well as the bulk of total SUMO conjugates in G(2)/M-arrested cells, indicating that sumoylated septins are the most abundant SUMO conjugates at this point in the cell cycle. This mutant has a striking defect in disassembly of septin rings, resulting in accumulation of septin rings marking previous division sites. Thus, SUMO conjugation plays a role in regulating septin ring dynamics during the cell cycle.
Figures


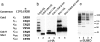

References
-
- Ausubel F.M., Brent R., Kingston R.E., Moore D.D., Smith J.A., Seidman J.G., Struhl K. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Wiley-Interscience; New York: 1994.
-
- Boeke J.D., LaCroute F., Fink G.R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5′-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1984;197:345–346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

