Automated thermal cycling is superior to traditional methods for nucleotide sequencing of bla(SHV) genes
- PMID: 10582889
- PMCID: PMC89594
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.43.12.2960
Automated thermal cycling is superior to traditional methods for nucleotide sequencing of bla(SHV) genes
Abstract
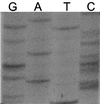
Genes encoding SHV-1 and SHV-2 were sequenced by different methods. Nucleotide sequencing of the coding strand by standard dideoxy-chain termination methods resulted in errors in the interpretation of the nucleotide sequence and the derived amino acid sequence in two main regions which corresponded to nucleotide and amino acid changes that had been reported previously. The automated thermal cycling method was clearly superior and consistently resulted in the correct sequences for these genes.
Figures


References
-
- Arakawa Y, Ohta M, Kido N, Fujii Y, Komatsu T, Kato N. Close evolutionary relationship between the chromosomally encoded β-lactamase gene of Klebsiella pneumoniae and the TEM β-lactamase gene mediated by R plasmids. FEBS Lett. 1986;207:69–74. - PubMed
-
- Arlet G, Rouveau M, Philippon A. Substitution of alanine for aspartate at position 179 in the SHV-6 extended-spectrum β-lactamase. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1997;152:163–167. - PubMed
-
- Barthélémy M, Péduzzi J, Yaghlane H B, Labia R. Single amino acid substitution between SHV-1 β-lactamase and cefotaxime-hydrolyzing SHV-2 enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1988;231:217–220. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

