Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of allopurinol in elderly and young subjects
- PMID: 10583019
- PMCID: PMC2014375
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1999.00041.x
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of allopurinol in elderly and young subjects
Abstract
Aims: The prevalence of hyperuricaemia and gout increases with age as does the incidence of adverse effects to allopurinol, the major uric acid lowering drug. The present study was performed to compare the disposition and effects of allopurinol and its active metabolite oxipurinol in elderly and young subjects without major health problems.
Methods: Ten elderly (age range 71-93 years) and nine young subjects (24-35 years) received an oral dose of 200 mg allopurinol in an open, single dose, cross sectional design. Four of these individuals were additionally dosed with 200 mg allopurinol intravenously. Plasma and urine concentrations of allopurinol, oxipurinol, hypoxanthine, xanthine, and uric acid were measured by h. p.l.c.
Results: Total clearance of allopurinol was not different in elderly (15.7+/-3.8 ml min-1 kg-1, mean+/-s.e. mean) and young subjects (15.7+/-2.1), whereas total clearance of oxipurinol was significantly reduced in the aged (0.24+/-0.03) compared with young controls (0.37+/-0.05) as was the distribution volume of oxipurinol (0.60+/-0.09 and 0.84+/-0.07 l kg-1, respectively). Oxipurinol was eliminated primarily by the kidneys, allopurinol by metabolism. Fractional peroral bioavailability of allopurinol was 0.81+/-0.16 (n=4, two elderly and two young subjects). Although maximal plasma concentrations of oxipurinol were significantly higher in elderly (5. 63+/-0.83 microgram ml-1 ) than in young persons (3.75+/-0.25) as was the area under the oxipurinol plasma concentration-time curve, AUC (260+/-46 and 166+/-23 microgram ml-1 h, respectively), the pharmacodynamic effect of oxipurinol was smaller in elderly than young subjects (time-dependent decrease of plasma uric acid 83+/-30 microgram ml-1 h in elderly compared with 176+/-21 in young controls). Oxipurinol increased the renal clearance of xanthine, suggesting inhibition of tubular xanthine reabsorption by oxipurinol.
Conclusions: Although allopurinol elimination is not reduced in the aged, that of its active metabolite oxipurinol is because of an age-dependent decline in renal function. Xanthine oxidase inhibition by oxipurinol appears to be reduced in old age. In addition to its uricostatic action, oxipurinol has a xanthinuric effect which is also diminished in the elderly.
Figures
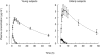
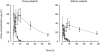
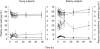
 ), (
), ( )), after oral administration of 200 mg allopurinol to elderly (solid symbols) and young subjects (open symbols). Note that the scale for hypoxanthine and xanthine (right y-axis) is 10-fold expanded compared with that for uric acid. Values are means±s.e. mean.
)), after oral administration of 200 mg allopurinol to elderly (solid symbols) and young subjects (open symbols). Note that the scale for hypoxanthine and xanthine (right y-axis) is 10-fold expanded compared with that for uric acid. Values are means±s.e. mean.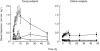
References
-
- Rundles RW. The development of allopurinol. Arch Intern Med. 1985;145:1492–1503. - PubMed
-
- Elion GB. The purine path to chemotherapy. Science. 1989;244:41–47. - PubMed
-
- Day RO, Birkett DJ, Hicks M, Miners JO, Graham GG, Brooks PM. New uses for allopurinol. Drugs. 1994;48:339–344. - PubMed
-
- Stewart R, Yost R, Hale W, Marks R. Epidemiology of hyperuricemia in an ambulatory elderly population. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1979;27:552–554. - PubMed
-
- Doherty M, Dieppe P. Crystal deposition disease in the elderly. Clin Rheumatol. 1986;12:97–116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

