Histidine-rich glycoprotein prevents the formation of insoluble immune complexes by rheumatoid factor
- PMID: 10583608
- PMCID: PMC2326949
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00885.x
Histidine-rich glycoprotein prevents the formation of insoluble immune complexes by rheumatoid factor
Abstract
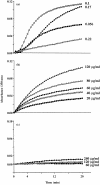
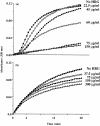
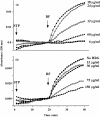
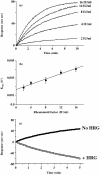
In previous studies we have shown that histidine-rich glycoprotein (HRG), a relatively abundant plasma protein, can bind to immunoglobulin G (IgG) and inhibit the insolubilization of IgG-containing immune complexes (IC). It was of interest, therefore, to determine whether HRG can inhibit the formation of insoluble IC (IIC) resulting from the interaction of rheumatoid factor (RF) with human IgG-containing IC. Light scattering techniques were used to examine the effect of HRG on the formation of IIC between RF and IC containing human IgG according to three different models. In all three models physiological concentrations of HRG could block the formation of IIC induced by RF. Optical biosensor studies of the RF-IgG interaction also revealed that HRG can mask the epitopes on IgG recognized by RF. Additional studies examined whether HRG can solubilize already formed IIC and demonstrated that HRG can, in fact, partially solubilized IIC. These data indicate that HRG can regulate the formation of IIC induced by RF at three levels: namely by inhibiting the initial recognition of IgG containing IC by RF, by inhibiting the subsequent insolubilization of IgG containing IC by RF and by solubilizing already formed IIC. Collectively, these findings suggest that HRG may be an important inhibitor of the formation of pathogenic IC in diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histidine-rich glycoprotein modulation of immune/autoimmune, vascular, and coagulation systems.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2008 Jun;34(3):307-12. doi: 10.1007/s12016-007-8058-6. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18219588 Review.
-
Histidine-rich glycoprotein regulates the binding of monomeric IgG and immune complexes to monocytes.Int Immunol. 1999 Aug;11(8):1275-82. doi: 10.1093/intimm/11.8.1275. Int Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10421785
-
Histidine-rich glycoprotein binds to human IgG and C1q and inhibits the formation of insoluble immune complexes.Biochemistry. 1997 Jun 3;36(22):6653-62. doi: 10.1021/bi962573n. Biochemistry. 1997. PMID: 9184145
-
Interference of rheumatoid factor activity by aspartame, a dipeptide methyl ester.J Mol Recognit. 1999 Jul-Aug;12(4):249-57. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1352(199907/08)12:4<249::AID-JMR463>3.0.CO;2-B. J Mol Recognit. 1999. Corrected and republished in: J Mol Recognit. 1999 Sep-Oct;12(5):249-57. PMID: 10440996 Corrected and republished.
-
Development of rheumatoid factor research through 50 years.Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1988;75:2-12. doi: 10.3109/03009748809096732. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1988. PMID: 3070723 Review.
Cited by
-
Histidine-rich glycoprotein (HRGP): Pleiotropic and paradoxical effects on macrophage, tumor microenvironment, angiogenesis, and other physiological and pathological processes.Genes Dis. 2020 Aug 8;9(2):381-392. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2020.07.015. eCollection 2022 Mar. Genes Dis. 2020. PMID: 35224154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Regulation of the Plasma Protein Histidine-Rich Glycoprotein by Zn2+ in Settings of Tissue Injury.Biomolecules. 2017 Mar 2;7(1):22. doi: 10.3390/biom7010022. Biomolecules. 2017. PMID: 28257077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histidine-rich glycoprotein modulation of immune/autoimmune, vascular, and coagulation systems.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2008 Jun;34(3):307-12. doi: 10.1007/s12016-007-8058-6. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18219588 Review.
-
Histidine-rich glycoprotein binds fibrin(ogen) with high affinity and competes with thrombin for binding to the gamma'-chain.J Biol Chem. 2011 Sep 2;286(35):30314-30323. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.253831. Epub 2011 Jul 8. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21757718 Free PMC article.
-
Polyphosphate-induced thrombosis in mice is factor XII dependent and is attenuated by histidine-rich glycoprotein.Blood Adv. 2021 Sep 28;5(18):3540-3551. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021004567. Blood Adv. 2021. PMID: 34474475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Panush RS, Bianco NE, Schur DH. Serum and synovial fluid IgG, IgA, and IgM anti‐immunoglobulins in rheumatoid arthritis. Arth Rheum. 1971;14:737. - PubMed
-
- Stewart JJ, Agosto H, Litwin S, et al. A solution to the rheumatoid paradox – pathologic rheumatoid factors can be tolerized by competition with natural rheumatoid factors. J Immunol. 1997;159:1728. - PubMed
-
- Johnson PM, Page Faulk W. Rheumatoid factor: its nature, specificity, and production in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976;6:414. - PubMed
-
- Capra JD, Winchester RJ, Kunkel HG. Cold‐reactive rheumatoid factors in infectious mononucleosis and other diseases. Arthr Rheum. 1969;12:67. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

