Biosynthesis of novel exopolymers by Aureobasidium pullulans
- PMID: 10583975
- PMCID: PMC91715
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.12.5265-5271.1999
Biosynthesis of novel exopolymers by Aureobasidium pullulans
Abstract
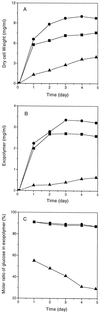
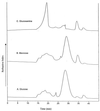
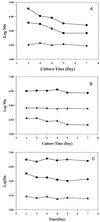
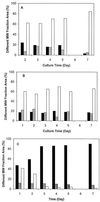
Aureobasidium pullulans ATCC 42023 was cultured under aerobic conditions with glucose, mannose, and glucose analogs as energy sources. The exopolymer extracts produced under these conditions were composed of glucose and mannose. The molar ratio of glucose to mannose in the exopolymer extract and the molecular weight of the exopolymer varied depending on the energy source and culture time. The glucose content of exopolymer extracts formed with glucose and mannose as the carbon sources was between 91 and 87%. The molecular weight decreased from 3.5 x 10(6) to 2.12 x 10(6) to 0.85 x 10(6) to 0.77 x 10(6) with culture time. As the culture time increased, the glucose content of the exopolymer extract formed with glucosamine decreased from 55 +/- 3 to 29 +/- 2 mol%, and the molecular weight increased from 2.73 x 10(6) to 4.86 x 10(6). There was no evidence that glucosamine was directly incorporated into exopolymers. The molar ratios of glucose to mannose in exopolymer extracts ranged from 87 +/- 3:13 +/- 3 to 28 +/- 2:72 +/- 2 and were affected by the energy source added. On the basis of the results of an enzyme hydrolysis analysis of the exopolymer extracts and the compositional changes observed, mannose (a repeating unit) was substituted for glucose, which gave rise to a new family of exopolymer analogs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New exopolysaccharides produced by Aureobasidium pullulans grown on glucosamine.Carbohydr Res. 2002 Jul 16;337(13):1203-9. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(02)00125-8. Carbohydr Res. 2002. PMID: 12110195
-
Modelling of simultaneous production of polygalacturonase and exopolysaccharide by Aureobasidium pullulans ATHUM 2915.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1998 Feb;73(2):155-62. doi: 10.1023/a:1000657403593. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1998. PMID: 9717573
-
Ascorbic acid stimulation of production of a highly branched ,beta-1,3-glucan by Aureobasidium pullulans K-1--oxalic acid, a metabolite of ascorbic acid as the stimulating substance.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2000 Sep;64(9):1801-6. doi: 10.1271/bbb.64.1801. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2000. PMID: 11055380
-
Inhibitors of the biosynthesis and processing of N-linked oligosaccharides.CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;16(1):21-49. doi: 10.3109/10409238409102805. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984. PMID: 6232113 Review.
-
LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL.Science. 1964 Aug 21;145(3634):783-9. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3634.783. Science. 1964. PMID: 14163315 Review.
Cited by
-
Biofabrication of Functional Pullulan by Aureobasidium pullulans under the Effect of Varying Mineral Salts and Sugar Stress Conditions.Molecules. 2023 Mar 8;28(6):2478. doi: 10.3390/molecules28062478. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36985449 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis and hyper production of pullulan by a newly isolated strain of Aspergillus japonicus-VIT-SB1.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Jul;30(7):2045-52. doi: 10.1007/s11274-014-1629-9. Epub 2014 Mar 8. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24609496
-
Production of pullulan by a thermotolerant aureobasidium pullulans strain in non-stirred fed batch fermentation process.Braz J Microbiol. 2012 Jul;43(3):1042-50. doi: 10.1590/S1517-838220120003000030. Epub 2012 Jun 1. Braz J Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 24031927 Free PMC article.
-
Direct incorporation of glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine into exopolymers by Gluconacetobacter xylinus (=Acetobacter xylinum) ATCC 10245: production of chitosan-cellulose and chitin-cellulose exopolymers.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001 Sep;67(9):3970-5. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.9.3970-3975.2001. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11525993 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient production of pullulan by Aureobasidium pullulans grown on mixtures of potato starch hydrolysate and sucrose.Braz J Microbiol. 2017 Jan-Mar;48(1):180-185. doi: 10.1016/j.bjm.2016.11.001. Epub 2016 Nov 19. Braz J Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 27923548 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Auer D P F, Seviour R J. Influence of varying nitrogen sources on polysaccharide production by Aureobasidium pullulans in batch culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1990;32:637–644.
-
- Badr-Eldin S M, El-Tayeb O M, El-Masry E G, Mohamad O A, El-Rahman O A A. Polysaccharide production by Aureobasidium pullulans: factors affecting polysaccharide formation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 1994;10:423–426. - PubMed
-
- Bouveng H O, Kiessling H, Lindberg B, McKay J. Polysaccharides elaborated by Pullularia pullulans. Acta Chem Scand. 1963;17:797–800.
-
- Catley B J. Pullulan, a relationship between molecular weight and fine structure. FEBS Lett. 1970;10:190–193. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

