Mitochondrial function in cell wall glycoprotein synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae NCYC 625 (Wild type) and [rho(0)] mutants
- PMID: 10583995
- PMCID: PMC91735
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.12.5398-5402.1999
Mitochondrial function in cell wall glycoprotein synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae NCYC 625 (Wild type) and [rho(0)] mutants
Abstract
We studied phosphopeptidomannans (PPMs) of two Saccharomyces cerevisiae NCYC 625 strains (S. diastaticus): a wild type strain grown aerobically, anaerobically, and in the presence of antimycin and a [rho(0)] mutant grown aerobically and anaerobically. The aerobic wild-type cultures were highly flocculent, but all others were weakly flocculent. Ligands implicated in flocculation of mutants or antimycin-treated cells were not aggregated as much by concanavalin A as were those of the wild type. The [rho(0)] mutants and antimycin-treated cells differ from the wild type in PPM composition and invertase, acid phosphatase, and glucoamylase activities. PPMs extracted from different cells differ in the protein but not in the glycosidic moiety. The PPMs were less stable in mitochondrion-deficient cells than in wild-type cells grown aerobically, and this difference may be attributable to defective mitochondrial function during cell wall synthesis. The reduced flocculation of cells grown in the presence of antimycin, under anaerobiosis, or carrying a [rho(0)] mutation may be the consequence of alterations of PPM structures which are the ligands of lectins, both involved in this cell-cell recognition phenomenon. These respiratory chain alterations also affect peripheral, biologically active glycoproteins such as extracellular enzymes and peripheral PPMs.
Figures
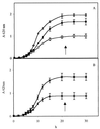
 , wild-type cells grown in aerobiosis and anaerobiosis, respectively;
, wild-type cells grown in aerobiosis and anaerobiosis, respectively;  and
and  , [rho0] mutant cells grown in aerobiosis and anaerobiosis, respectively. Results are expressed as percentages of the total amino acid content.
, [rho0] mutant cells grown in aerobiosis and anaerobiosis, respectively. Results are expressed as percentages of the total amino acid content.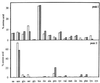
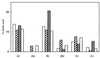
 , wild-type and [rho0] mutant cells grown in aerobiosis, respectively. Results are expressed as percentages of the total amino acid content.
, wild-type and [rho0] mutant cells grown in aerobiosis, respectively. Results are expressed as percentages of the total amino acid content.References
-
- Ballou C E. Isolation, characterization and properties of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mnn mutants with non-conditional protein glycosylation defects. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:440–470. - PubMed
-
- Calleja G B. Role of mitochondria in the sex-directed flocculation of a yeast. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973;154:382–386. - PubMed
-
- Donzeau M, Bourdineaud J P, Lauquin G J M. Regulation by low temperatures and anaerobiosis of a yeast gene specifying a putative GPI-anchored plasma membrane protein. Mol Microbiol. 1996;20:449–459. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

