RIBP, a novel Rlk/Txk- and itk-binding adaptor protein that regulates T cell activation
- PMID: 10587356
- PMCID: PMC2195727
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.190.11.1657
RIBP, a novel Rlk/Txk- and itk-binding adaptor protein that regulates T cell activation
Abstract
A novel T cell-specific adaptor protein, RIBP, was identified based on its ability to bind Rlk/Txk in a yeast two-hybrid screen of a mouse T cell lymphoma library. RIBP was also found to interact with a related member of the Tec family of tyrosine kinases, Itk. Expression of RIBP is restricted to T and natural killer cells and is upregulated substantially after T cell activation. RIBP-disrupted knockout mice displayed apparently normal T cell development. However, proliferation of RIBP-deficient T cells in response to T cell receptor (TCR)-mediated activation was significantly impaired. Furthermore, these activated T cells were defective in the production of interleukin (IL)-2 and interferon gamma, but not IL-4. These data suggest that RIBP plays an important role in TCR-mediated signal transduction pathways and that its binding to Itk and Rlk/Txk may regulate T cell differentiation.
Figures


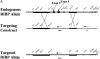
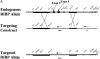



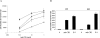
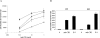
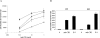
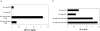
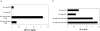
References
-
- Chan A.C., Shaw A.S. Regulation of antigen receptor signal transduction by protein tyrosine kinases. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1996;8:394–401. - PubMed
-
- Bolen J.B. Protein tyrosine kinases in the initiation of antigen receptor signaling. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1995;7:306–311. - PubMed
-
- DeFranco A.L. Transmembrane signaling by antigen receptors of B and T lymphocytes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1995;7:163–175. - PubMed
-
- Weiss A., Littman D.R. Signal transduction by lymphocyte antigen receptors. Cell. 1994;76:263–274. - PubMed
-
- Neet K., Hunter T. Vertebrate non-receptor protein-tyrosine kinase families. Genes Cells. 1996;1:147–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

