Mice transgenic for BAFF develop lymphocytic disorders along with autoimmune manifestations
- PMID: 10587360
- PMCID: PMC2195729
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.190.11.1697
Mice transgenic for BAFF develop lymphocytic disorders along with autoimmune manifestations
Abstract
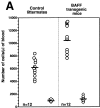
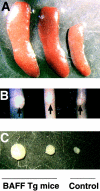
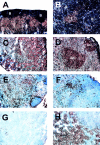
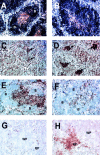
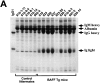
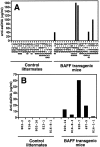
The cause of many autoimmune and inflammatory diseases is unresolved, although dysregulated production of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family members appears to be important in many cases. BAFF, a new member of the TNF family, binds to B cells and costimulates their growth in vitro. Mice transgenic for BAFF have vastly increased numbers of mature B and effector T cells, and develop autoimmune-like manifestations such as the presence of high levels of rheumatoid factors, circulating immune complexes, anti-DNA autoantibodies, and immunoglobulin deposition in the kidneys. This phenotype is reminiscent of certain human autoimmune disorders and suggests that dysregulation of BAFF expression may be a critical element in the chain of events leading to autoimmunity.
Figures









References
-
- Goodnow C.C., Cyster J.G., Hartley S.B., Bell S.E., Cooke M.P., Healy J.I., Akkaraju S., Rathmell J.C., Pogue S.L., Shokat K.P. Self-tolerance check points in B cell development. Adv. Immunol. 1995;59:279–369. - PubMed
-
- Miller J.F., Basten A. Mechanisms of tolerance to self. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1996;8:815–821. - PubMed
-
- McDevitt H.O., Wakeland E.K. Autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1998;10:647–648. - PubMed
-
- Rose N.R. The role of infection in the pathogenesis of autoimmune disease. Semin. Immunol. 1998;10:5–13. - PubMed
-
- Fox D. The role of T cells in the immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40:598–609. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

