Mutations in the cardiac transcription factor NKX2.5 affect diverse cardiac developmental pathways
- PMID: 10587520
- PMCID: PMC409866
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI8154
Mutations in the cardiac transcription factor NKX2.5 affect diverse cardiac developmental pathways
Abstract
Heterozygous mutations in NKX2.5, a homeobox transcription factor, were reported to cause secundum atrial septal defects and result in atrioventricular (AV) conduction block during postnatal life. To further characterize the role of NKX2.5 in cardiac morphogenesis, we sought additional mutations in groups of probands with cardiac anomalies and first-degree AV block, idiopathic AV block, or tetralogy of Fallot. We identified 7 novel mutations by sequence analysis of the NKX2.5-coding region in 26 individuals. Associated phenotypes included AV block, which was the primary manifestation of cardiac disease in nearly a quarter of affected individuals, as well as atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defect. Ventricular septal defect was associated with tetralogy of Fallot or double-outlet right ventricle in 3 individuals. Ebstein's anomaly and other tricuspid valve abnormalities were also present. Mutations in human NKX2.5 cause a variety of cardiac anomalies and may account for a clinically significant portion of tetralogy of Fallot and idiopathic AV block. The coinheritance of NKX2.5 mutations with various congenital heart defects suggests that this transcription factor contributes to diverse cardiac developmental pathways.
Figures


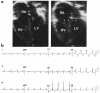
Comment in
-
Single allele mutations at the heart of congenital disease.J Clin Invest. 1999 Dec;104(11):1483-4. doi: 10.1172/JCI8825. J Clin Invest. 1999. PMID: 10587507 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Olson EN, Srivastava D. Molecular pathways controlling heart development. Science. 1996;272:671–676. - PubMed
-
- Harvey RD. Nk-2 homeobox genes and heart development. Dev Biol. 1996;178:203–216. - PubMed
-
- Fishman MC, Olson EN. Parsing the heart: genetic modules for organ assembly. Cell. 1997;91:153–156. - PubMed
-
- Bodmer R. The gene, tinman, is required for specification of the heart and visceral muscles in Drosophilia. Development. 1993;118:719–729. - PubMed
-
- Lints TJ, Parsons LM, Hartley L, Lyons I, Harvey RP. Nkx 2-5: a novel murine homeobox gene expressed in early heart progenitor cells and their myogenic descendents. Development. 1993;119:419–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

