Sound- and pressure-induced vertigo associated with dehiscence of the roof of the superior semicircular canal
- PMID: 10588128
- PMCID: PMC7657793
Sound- and pressure-induced vertigo associated with dehiscence of the roof of the superior semicircular canal
Abstract
In many types of peripheral vertigo, imaging is not part of the initial evaluation. We present a patient with sound- and pressure-induced vertigo associated with bony dehiscence of the roof of the superior semicircular canal. The diagnosis of this new entity can only be made by high-resolution coronal CT imaging of the temporal bones. In patients with this symptom complex, CT should be performed early in the diagnostic workup.
Figures
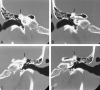
Similar articles
-
CT evaluation of bone dehiscence of the superior semicircular canal as a cause of sound- and/or pressure-induced vertigo.Radiology. 2003 Feb;226(2):337-43. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2262010897. Radiology. 2003. PMID: 12563123
-
Semicircular canal dehiscence in HR multislice computed tomography: distribution, frequency, and clinical relevance.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012 Feb;269(2):475-80. doi: 10.1007/s00405-011-1688-6. Epub 2011 Jul 8. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012. PMID: 21739095
-
Superior semicircular canal dehiscence syndrome and multi-detector row CT.Radiology. 2003 Feb;226(2):312-4. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2262021327. Radiology. 2003. PMID: 12563121 No abstract available.
-
Another etiology for vertigo due to idiopathic lateral semicircular canal bony defect.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2011 Jun;38(3):402-5. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2010.11.003. Epub 2011 Jan 7. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2011. PMID: 21216120 Review.
-
Superior semicircular canal dehiscence: Diagnosis and management.J Clin Neurosci. 2018 Feb;48:58-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2017.11.019. Epub 2017 Dec 7. J Clin Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29224712 Review.
Cited by
-
Semicircular canal dehiscence: comparison of T2-weighted turbo spin-echo MRI and CT.Neuroradiology. 2004 Apr;46(4):326-31. doi: 10.1007/s00234-003-0948-6. Epub 2004 Mar 13. Neuroradiology. 2004. PMID: 15024531
-
Vertigo and hearing loss.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009 Sep;30(8):1623-5. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009. PMID: 19749077 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Recent surgical options for vestibular vertigo.GMS Curr Top Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Dec 18;16:Doc01. doi: 10.3205/cto000140. eCollection 2017. GMS Curr Top Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017. PMID: 29279721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Superior semicircular canal dehiscence: a radiological and clinical study.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024 Feb;76(1):865-870. doi: 10.1007/s12070-023-04299-8. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024. PMID: 38440643 Free PMC article.
-
Superior Canal Dehiscence Syndrome.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2006 May-Jun;72(3):414-8. doi: 10.1016/s1808-8694(15)30978-2. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2006. PMID: 17119781 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fox EJ, Balkany TJ, Arenberg IK, The Tullio phenomenon and perilymph fistula. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1988;98:88-89 - PubMed
-
- Kacker SK, Hinchcliffe T, Unusual Tullio phenomena. J Laryngol Otol 1970;84:155-166 - PubMed
-
- Kwee HL, The occurrence of the Tullio phenomenon in congenitally deaf children. J Laryngol Otol 1976;90:501-507 - PubMed
-
- Ishizaki H, Pyykko I, Aalto H, Starck J, The Tullio phenomenon and postural stability: experimental study in normal subjects and patients with vertigo. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1991;100:976-983 - PubMed
-
- Nields JA, Kveton JF, Tullio phenomenon and seronegative Lyme borreliosis. Lancet 1991;338:128-129 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
