Phosphorylation of SNAP-23 by the novel kinase SNAK regulates t-SNARE complex assembly
- PMID: 10588641
- PMCID: PMC25741
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.12.4033
Phosphorylation of SNAP-23 by the novel kinase SNAK regulates t-SNARE complex assembly
Abstract
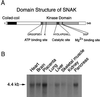
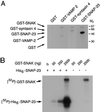
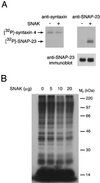
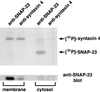
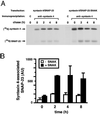
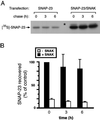
The docking and fusion of cargo-containing vesicles with target membranes of eukaryotic cells is mediated by the interaction of SNARE proteins present on both vesicle and target membranes. In many cases, the target membrane SNARE, or t-SNARE, exists as a complex of syntaxin with a member of the SNAP-25 family of palmitoylated proteins. We have identified a novel human kinase SNAK (SNARE kinase) that specifically phosphorylates the nonneuronal t-SNARE SNAP-23 in vivo. Interestingly, only SNAP-23 that is not assembled into t-SNARE complexes is phosphorylated by SNAK, and phosphorylated SNAP-23 resides exclusively in the cytosol. Coexpression with SNAK significantly enhances the stability of unassembled SNAP-23, and as a consequence, the assembly of newly synthesized SNAP-23 with syntaxin is augmented. These data demonstrate that phosphorylation of SNAP-23 by SNAK enhances the kinetics of t-SNARE assembly in vivo.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson HA, Roche PA. Phosphorylation regulates the delivery of MHC class II invariant chain complexes to antigen processing compartments. J Immunol. 1998;160:4850–4858. - PubMed
-
- Araki S, Tamori Y, Kawanishi M, Shinoda H, Masugi J, Mori H, Niki T, Okazawa H, Kubota T, Kasuga M. Inhibition of the binding of SNAP-23 to syntaxin 4 by Munc18c. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;234:257–262. - PubMed
-
- Bennett MK, Scheller RH. A molecular description of synaptic vesicle membrane trafficking. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:63–100. - PubMed
-
- Brennwald P, Kearns B, Champion K, Keranen S, Bankaitis V, Novick P. Sec9 is a SNAP-25-like component of a yeast SNARE complex that may be the effector of Sec4 function in exocytosis. Cell. 1994;79:245–258. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

