Imaging of biological macromolecules on mica in humid air by scanning electrochemical microscopy
- PMID: 10588687
- PMCID: PMC24418
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.25.14222
Imaging of biological macromolecules on mica in humid air by scanning electrochemical microscopy
Abstract
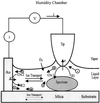
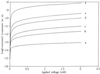
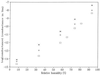
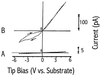
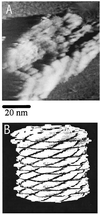
Imaging of DNA, keyhole limpet hemocyanin, mouse monoclonal IgG, and glucose oxidase on a mica substrate has been accomplished by scanning electrochemical microscopy with a tungsten tip. The technique requires the use of a high relative humidity to form a thin film of water on the mica surface that allows electrochemical reactions to take place at the tip and produce a faradaic current (approximately 1 pA) that can be used to control tip position. The effect of relative humidity and surface pretreatment with buffer solutions on the ionic conductivity of a mica surface was investigated to find appropriate conditions for imaging. Resolution of the order of 1 nm was obtained.
Figures
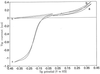
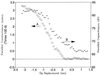

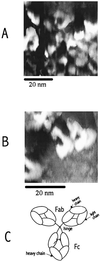
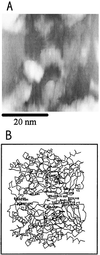
Comment in
-
Varieties of imaging with scanning probe microscopes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Dec 21;96(26):14678-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.26.14678. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10611271 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wickramasinghe H K, editor. Scanned Probe Microscopy, American Institute of Physics Conference Proceedings 241. New York: American Institute of Physics; 1992.
-
- Bard A J, Fan F-R, Mirkin M V. In: Electroanalytical Chemistry. Bard A J, editor. Vol. 18. New York: Dekker; 1994. pp. 243–373.
-
- Guckenberger R, Heim M, Ceve G, Knapp H, Wiegräbe W, Hillebrand A. Science. 1994;266:1538–1540. - PubMed
-
- Fan F-R F, Bard A J. Science. 1995;270:1849–1851. - PubMed
-
- Forouzan F, Bard A J. J Phys Chem. 1997;101:10876–10879.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

