The polo-box-dependent induction of ectopic septal structures by a mammalian polo kinase, plk, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 10588710
- PMCID: PMC24441
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.25.14360
The polo-box-dependent induction of ectopic septal structures by a mammalian polo kinase, plk, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
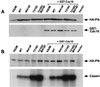
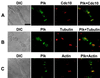
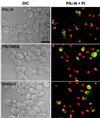
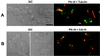
Members of the polo subfamily of protein kinases play pivotal roles in cell-cycle control and proliferation. In addition to a high degree of sequence similarity in the kinase domain, polo kinases contain a strikingly conserved motif termed "polo-box" in the noncatalytic C-terminal domain. We have previously shown that the mammalian polo-like kinase Plk is a functional homolog of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cdc5. Here, we show that, in a polo-box- and kinase activity-dependent manner, ectopic expression of Plk in budding yeast can induce a class of cells with abnormally elongated buds. In addition to localization at spindle poles and cytokinetic neck filaments, Plk induces and localizes to ectopic septin ring structures within the elongated buds. In contrast, mutations in the polo-box abolish both localization to, and induction of, septal structures. Consistent with the polo-box-dependent subcellular localization, the C-terminal domain of Plk, but not its polo-box mutant, is sufficient for subcellular localization. Our data suggest that Plk may contribute a signal to initiate or promote cytokinetic event(s) and that an intact polo-box is required for regulation of these cellular processes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Essential function of the polo box of Cdc5 in subcellular localization and induction of cytokinetic structures.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Jan;20(1):286-98. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.1.286-298.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10594031 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of the polo-box disrupts localization and mitotic functions of the mammalian polo kinase Plk.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Aug 4;95(16):9301-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.16.9301. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9689075 Free PMC article.
-
Plk is a functional homolog of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cdc5, and elevated Plk activity induces multiple septation structures.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Jun;17(6):3408-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.6.3408. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9154840 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and enzoinformatics perspectives of targeting Polo-like kinase 1 in cancer therapy.Semin Cancer Biol. 2019 Jun;56:47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.11.004. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019. PMID: 29122685 Review.
-
The family of polo-like kinases.Prog Cell Cycle Res. 1996;2:107-14. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-5873-6_11. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 1996. PMID: 9552388 Review.
Cited by
-
Peripheral Golgi protein GRASP65 is a target of mitotic polo-like kinase (Plk) and Cdc2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Nov 7;97(23):12589-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.220423497. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 11050165 Free PMC article.
-
Functional dynamics of Polo-like kinase 1 at the centrosome.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Jun;29(11):3134-50. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01663-08. Epub 2009 Mar 23. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19307309 Free PMC article.
-
The Polo-like kinase Cdc5 interacts with FEAR network components and Cdc14.Cell Cycle. 2008 Oct;7(20):3262-72. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.20.6852. Epub 2008 Oct 25. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18927509 Free PMC article.
-
Oscillations in Cdc14 release and sequestration reveal a circuit underlying mitotic exit.J Cell Biol. 2010 Jul 26;190(2):209-22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201002026. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20660629 Free PMC article.
-
A novel function of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CDC5 in cytokinesis.J Cell Biol. 2001 Feb 5;152(3):451-69. doi: 10.1083/jcb.152.3.451. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11157974 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

