Soluble complexes of regulated upon activation, normal T cells expressed and secreted (RANTES) and glycosaminoglycans suppress HIV-1 infection but do not induce Ca(2+) signaling
- PMID: 10588734
- PMCID: PMC24465
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.25.14499
Soluble complexes of regulated upon activation, normal T cells expressed and secreted (RANTES) and glycosaminoglycans suppress HIV-1 infection but do not induce Ca(2+) signaling
Abstract
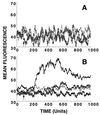
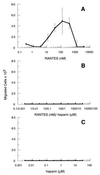
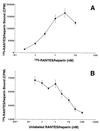
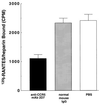
Chemokines comprise a family of low-molecular-weight proteins that elicit a variety of biological responses including chemotaxis, intracellular Ca(2+) mobilization, and activation of tyrosine kinase signaling cascades. A subset of chemokines, including regulated upon activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted (RANTES), macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha (MIP-1alpha), and MIP-1beta, also suppress infection by HIV-1. All of these activities are contingent on interactions between chemokines and cognate seven-transmembrane spanning, G protein-coupled receptors. However, these activities are strongly inhibited by glycanase treatment of receptor-expressing cells, indicating an additional dependence on surface glycosaminoglycans (GAG). To further investigate this dependence, we examined whether soluble GAG could reconstitute the biological activities of RANTES on glycanase-treated cells. Complexes formed between RANTES and a number of soluble GAG failed to induce intracellular Ca(2+) mobilization on either glycanase-treated or untreated peripheral blood mononuclear cells and were unable to stimulate chemotaxis. In contrast, the same complexes demonstrated suppressive activity against macrophage tropic HIV-1. Complexes composed of (125)I-labeled RANTES demonstrated saturable binding to glycanase-treated peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and such binding could be reversed partially by an anti-CCR5 antibody. These results suggest that soluble chemokine-GAG complexes represent seven-transmembrane ligands that do not activate receptors yet suppress HIV infection. Such complexes may be considered as therapeutic formulations for the treatment of HIV-1 infection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Soluble glycosaminoglycans Do not potentiate RANTES antiviral activity on the infection of primary macrophages by human immunodeficiency virus type 1.Virology. 2000 Dec 20;278(2):412-22. doi: 10.1006/viro.2000.0670. Virology. 2000. PMID: 11118364
-
Limited expression of R5-tropic HIV-1 in CCR5-positive type 1-polarized T cells explained by their ability to produce RANTES, MIP-1alpha, and MIP-1beta.Blood. 2000 Feb 15;95(4):1167-74. Blood. 2000. PMID: 10666186
-
Examination of the function of RANTES, MIP-1alpha, and MIP-1beta following interaction with heparin-like glycosaminoglycans.J Biol Chem. 2000 Apr 21;275(16):11721-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.16.11721. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10766793
-
Increased replication of T-cell-tropic HIV strains and CXC-chemokine receptor-4 induction in T cells treated with macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1alpha, MIP-1beta and RANTES beta-chemokines.AIDS. 1998 Jan 22;12(2):183-90. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199802000-00008. AIDS. 1998. PMID: 9468367
-
In vivo evolution of HIV-1 co-receptor usage and sensitivity to chemokine-mediated suppression.Nat Med. 1997 Nov;3(11):1259-65. doi: 10.1038/nm1197-1259. Nat Med. 1997. PMID: 9359702
Cited by
-
Noncytolytic inhibition of X4 virus by bulk CD8(+) cells from human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-infected persons and HIV-1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes is not mediated by beta-chemokines.J Virol. 2001 Sep;75(17):8306-16. doi: 10.1128/jvi.75.17.8306-8316.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11483776 Free PMC article.
-
Noninfectious papilloma virus-like particles inhibit HIV-1 replication: implications for immune control of HIV-1 infection by IL-27.Blood. 2007 Mar 1;109(5):1841-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-02-001578. Epub 2006 Oct 26. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17068156 Free PMC article.
-
Taking a hard look at the pathogenesis of childhood HIV-associated nephropathy.Pediatr Nephrol. 2009 Nov;24(11):2109-19. doi: 10.1007/s00467-009-1155-4. Epub 2009 Mar 14. Pediatr Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19288142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potent, broad-spectrum inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by the CCR5 monoclonal antibody PRO 140.J Virol. 2001 Jan;75(2):579-88. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.2.579-588.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11134270 Free PMC article.
-
GAG-DB, the New Interface of the Three-Dimensional Landscape of Glycosaminoglycans.Biomolecules. 2020 Dec 11;10(12):1660. doi: 10.3390/biom10121660. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33322545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baggiolini M. Nature (London) 1998;392:565–568. - PubMed
-
- Alkhatib G, Combadiere C, Broder C C, Feng Y, Kennedy P E, Murphy P M, Berger E A. Science. 1996;272:1955–1958. - PubMed
-
- Choe H, Farzan M, Sun Y, Sullivan N, Rollins B, Ponath P D, Wu L, Mackay C R, LaRosa G, Newman W, et al. Cell. 1996;85:1135–1148. - PubMed
-
- Deng H, Liu R, Ellmeier W, Choe S, Unutmaz D, Burkhart M, Di Marzio P, Marmon S, Sutton R E, Hill C M, et al. Nature (London) 1996;381:661–666. - PubMed
-
- Doranz B J, Rucker J, Yi Y, Smyth R J, Samson M, Peiper S C, Parmentier M, Collman R G, Doms R W. Cell. 1996;85:1149–1158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

