Mice mutant for glucokinase regulatory protein exhibit decreased liver glucokinase: a sequestration mechanism in metabolic regulation
- PMID: 10588736
- PMCID: PMC24467
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.25.14511
Mice mutant for glucokinase regulatory protein exhibit decreased liver glucokinase: a sequestration mechanism in metabolic regulation
Abstract
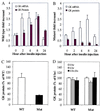
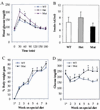
The importance of glucokinase (GK; EC 2.7.1.12) in glucose homeostasis has been demonstrated by the association of GK mutations with diabetes mellitus in humans and by alterations in glucose metabolism in transgenic and gene knockout mice. Liver GK activity in humans and rodents is allosterically inhibited by GK regulatory protein (GKRP). To further understand the role of GKRP in GK regulation, the mouse GKRP gene was inactivated. With the knockout of the GKRP gene, there was a parallel loss of GK protein and activity in mutant mouse liver. The loss was primarily because of posttranscriptional regulation of GK, indicating a positive regulatory role for GKRP in maintaining GK levels and activity. As in rat hepatocytes, both GK and GKRP were localized in the nuclei of mouse hepatocytes cultured in low-glucose-containing medium. In the presence of fructose or high concentrations of glucose, conditions known to relieve GK inhibition by GKRP in vitro, only GK was translocated into the cytoplasm. In the GKRP-mutant hepatocytes, GK was not found in the nucleus under any tested conditions. We propose that GKRP functions as an anchor to sequester and inhibit GK in the hepatocyte nucleus, where it is protected from degradation. This ensures that glucose phosphorylation is minimal when the liver is in the fasting, glucose-producing phase. This also enables the hepatocytes to rapidly mobilize GK into the cytoplasm to phosphorylate and store or metabolize glucose after the ingestion of dietary glucose. In GKRP-mutant mice, the disruption of this regulation and the subsequent decrease in GK activity leads to altered glucose metabolism and impaired glycemic control.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Insulin-receptor substrate-2 (irs-2) is required for maintaining glucokinase and glucokinase regulatory protein expression in mouse liver.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e58797. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058797. Epub 2013 Apr 1. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23560040 Free PMC article.
-
Glucokinase regulatory protein is essential for the proper subcellular localisation of liver glucokinase.FEBS Lett. 1999 Aug 6;456(2):332-8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00971-0. FEBS Lett. 1999. PMID: 10456334
-
An allosteric activator of glucokinase impairs the interaction of glucokinase and glucokinase regulatory protein and regulates glucose metabolism.J Biol Chem. 2006 Dec 8;281(49):37668-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605186200. Epub 2006 Oct 6. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 17028192
-
Recent Updates on Glucokinase Activators and Glucokinase Regulatory Protein Disrupters for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2019;15(3):205-212. doi: 10.2174/1573399814666180724100749. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2019. PMID: 30039763 Review.
-
Hormonal and Metabolite Regulation of Hepatic Glucokinase.Annu Rev Nutr. 2016 Jul 17;36:389-415. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-071715-051145. Epub 2016 May 4. Annu Rev Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27146014 Review.
Cited by
-
Glucotoxicity targets hepatic glucokinase in Zucker diabetic fatty rats, a model of type 2 diabetes associated with obesity.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Jun 1;306(11):E1225-38. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00507.2013. Epub 2014 Apr 8. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24714398 Free PMC article.
-
Association of GCKR rs780094, alone or in combination with GCK rs1799884, with type 2 diabetes and related traits in a Han Chinese population.Diabetologia. 2009 May;52(5):834-43. doi: 10.1007/s00125-009-1290-2. Epub 2009 Feb 25. Diabetologia. 2009. PMID: 19241058
-
Role of glucokinase in the subcellular localization of glucokinase regulatory protein.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Apr 2;16(4):7377-93. doi: 10.3390/ijms16047377. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25849650 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-receptor substrate-2 (irs-2) is required for maintaining glucokinase and glucokinase regulatory protein expression in mouse liver.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e58797. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058797. Epub 2013 Apr 1. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23560040 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of glucokinase regulatory protein expression may contribute to low glucokinase activity in feline liver.Vet Res Commun. 2009 Mar;33(3):227-40. doi: 10.1007/s11259-008-9171-6. Epub 2008 Sep 9. Vet Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 18780155
References
-
- Matschinsky F A. Diabetes. 1996;45:223–241. - PubMed
-
- Froguel P, Zouali H, Vionnet N, Velho G, Vaxillaire M, Sun F, Lesage S, Stoffel M, Takeda J, Passa P, et al. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:697–702. - PubMed
-
- Bali D, Svetlanov A, Lee H-W, Fusco-DeMane D, Leiser M, Li B, Barzilai N, Surana M, Hou H, Fleischer N, et al. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:21464–21467. - PubMed
-
- Grupe A, Hultgren B, Ryan A, Ma Y, Bauer M, Stewart T. Cell. 1995;83:69–78. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

