Altered states: involvement of phosphorylated CagA in the induction of host cellular growth changes by Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 10588744
- PMCID: PMC24475
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.25.14559
Altered states: involvement of phosphorylated CagA in the induction of host cellular growth changes by Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
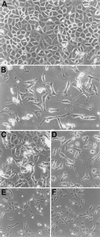
Helicobacter pylori, present in half of the world's population, is a very successful pathogen. It can survive for decades in the human stomach with few obvious consequences to the host. However, it is also the cause of gastric diseases ranging from gastritis to ulcers to gastric cancer and has been classified a type 1 carcinogen by the World Health Organization. We have previously shown that phosphorylation of a 145-kDa protein and activation of signal transduction pathways are associated with the attachment of H. pylori to gastric cells. Here we identify the 145-kDa protein as the H. pylori CagA protein. We also show that CagA is necessary to induce a growth-factor-like phenotype (hummingbird) in host gastric cells similar to that induced by hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). Additionally, we identify a second cellular phenotype induced after attachment by H. pylori, which we call SFA (stress fiber associated). SFA is CagA independent and is produced by type I and type II H. pylori.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

