A comprehensive approach to mapping the interacting surfaces of murine amphotropic and feline subgroup B leukemia viruses with their cell surface receptors
- PMID: 10590111
- PMCID: PMC111533
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.1.237-244.2000
A comprehensive approach to mapping the interacting surfaces of murine amphotropic and feline subgroup B leukemia viruses with their cell surface receptors
Abstract
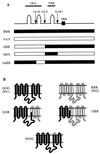
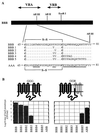
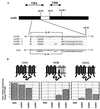
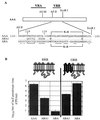
Because mutations in envelope glycoproteins of retroviruses or in their cell surface receptors can eliminate function by multiple mechanisms, it has been difficult to unambiguously identify sites for their interactions by site-directed mutagenesis. Recently, we developed a gain-of-function approach to overcome this problem. Our strategy relies on the fact that feline leukemia virus subgroup B (FeLV-B) and amphotropic murine leukemia virus (A-MLV) have closely related gp70 surface envelope glycoproteins and use related Na(+)-dependent phosphate symporters, Pit1 and Pit2, respectively, as their receptors. We previously observed that FeLV-B/A-MLV envelope glycoprotein chimeras spliced between the variable regions VRA and VRB were unable to use Pit1 or Pit2 as a receptor but could efficiently use specific Pit1/Pit2 chimeras. The latter study suggested that the VRA of A-MLV and FeLV-B functionally interact with the presumptive extracellular loops 4 and 5 (ECL4 and -5) of their respective receptors, whereas VRB interacts with ECL2. We also found that FeLV-B gp70 residues F60 and P61 and A-MLV residues Y60 and V61 in the first disulfide-bonded loop of VRA were important for functional interaction with the receptor's ECL4 or -5. We have now extended this approach to identify additional VRA and VRB residues that are involved in receptor recognition. Our studies imply that FeLV-B VRA residues F60 and P61 interact with the Pit1 ECL5 region, whereas VRA residues 66 to 78 interact with Pit1 ECL4. Correspondingly, A-MLV VRA residues Y60 and V61 interact with the Pit2 ECL5 region, whereas residues 66 to 78 interact with Pit2 ECL4. Similar studies that focused on the gp70 VRB implicated residues 129 to 139 as contributing to specific interactions with the receptor ECL2. These results identify three regions of gp70 that interact in a specific manner with distinct portions of their receptors, thereby providing a map of the functionally interacting surfaces.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Feline Pit2 functions as a receptor for subgroup B feline leukemia viruses.J Virol. 2001 Nov;75(22):10563-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.22.10563-10572.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11602698 Free PMC article.
-
Variable regions A and B in the envelope glycoproteins of feline leukemia virus subgroup B and amphotropic murine leukemia virus interact with discrete receptor domains.J Virol. 1997 Dec;71(12):9383-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.12.9383-9391.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9371598 Free PMC article.
-
Three distinct envelope domains, variably present in subgroup B feline leukemia virus recombinants, mediate Pit1 and Pit2 receptor recognition.J Virol. 1997 Nov;71(11):8116-23. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.11.8116-8123.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9343161 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of envelope determinants of feline leukemia virus subgroup B that permit infection and gene transfer to cells expressing human Pit1 or Pit2.J Virol. 2001 Aug;75(15):6841-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.15.6841-6849.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11435563 Free PMC article.
-
Xenotropism: the elusive viral receptor finally uncovered.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Feb 2;96(3):802-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.3.802. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 9927648 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The central half of Pit2 is not required for its function as a retroviral receptor.J Virol. 2004 Sep;78(17):9564-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.17.9564-9567.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15308749 Free PMC article.
-
Feline Pit2 functions as a receptor for subgroup B feline leukemia viruses.J Virol. 2001 Nov;75(22):10563-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.22.10563-10572.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11602698 Free PMC article.
-
Fusion-defective gibbon ape leukemia virus vectors can be rescued by homologous but not heterologous soluble envelope proteins.J Virol. 2002 May;76(9):4267-74. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.9.4267-4274.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11932392 Free PMC article.
-
G100R mutation within 4070A murine leukemia virus Env increases virus receptor binding, kinetics of entry, and viral transduction efficiency.J Virol. 2003 Jan;77(1):739-43. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.1.739-743.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12477879 Free PMC article.
-
Single-round selection yields a unique retroviral envelope utilizing GPR172A as its host receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Apr 7;106(14):5848-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809741106. Epub 2009 Mar 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19307586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atchison R E, Gosling J, Monteclaro F S, Franci C, Digilio L, Charo I F, Goldsmith M A. Multiple extracellular elements of CCR5 and HIV-1 entry: dissociation from response to chemokines. Science. 1996;274:1924–1926. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

