Inhibition of calpain blocks platelet secretion, aggregation, and spreading
- PMID: 10593923
- PMCID: PMC2727653
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.274.51.36321
Inhibition of calpain blocks platelet secretion, aggregation, and spreading
Abstract
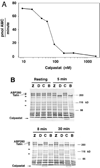
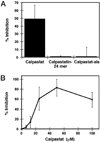
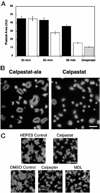
Previous studies have indicated that the Ca(2+)-dependent protease, calpain, is activated in platelets within 30-60 s of thrombin stimulation, but specific roles of calpain in platelets remain to be identified. To directly test the functions of calpain during platelet activation, a novel strategy was developed for introducing calpain's specific biological inhibitor, calpastatin, into platelets prior to activation. This method involves treatment of platelets with a fusion peptide, calpastat, consisting of the cell-penetrating signal sequence from Kaposi's fibroblast growth factor connected to a calpain-inhibiting consensus sequence derived from calpastatin. Calpastat specifically inhibits thrombin peptide (SFLLR)-induced alpha-granule secretion (IC(50) = 20 microM) during the first 30 s of activation, thrombin-induced platelet aggregation (IC(50) = 50 microM), and platelet spreading on glass surfaces (IC(50) = 34 microM). Calpastat-Ala, a mutant peptide in which alanine is substituted at conserved calpastatin residues, lacks calpain inhibitory activity and fails to inhibit secretion, aggregation, or spreading. The peptidyl calpain inhibitors calpeptin, MDL 28,170 (MDL) and E64d also inhibit secretion, aggregation and spreading, but require 3-10-fold higher concentrations than calpastat for biological activity. Together, these findings demonstrate that calpain regulates platelet secretion, aggregation, and spreading and indicate that calpain plays an earlier role in platelet activation following thrombin receptor stimulation than had been previously detected.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Calpain regulation of cytoskeletal signaling complexes in von Willebrand factor-stimulated platelets. Distinct roles for glycoprotein Ib-V-IX and glycoprotein IIb-IIIa (integrin alphaIIbbeta3) in von Willebrand factor-induced signal transduction.J Biol Chem. 1997 Aug 29;272(35):21847-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.35.21847. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9268316
-
Modulation of thrombin-induced platelet aggregation by inhibition of calpain by a synthetic peptide derived from the thiol-protease inhibitory sequence of kininogens and S-(3-nitro-2-pyridinesulfenyl)-cysteine.Eur J Biochem. 1993 May 15;214(1):233-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17916.x. Eur J Biochem. 1993. PMID: 8389701
-
The role of calpain in stimulus-response coupling: evidence that calpain mediates agonist-induced expression of procoagulant activity in platelets.Blood. 1990 Dec 15;76(12):2510-9. Blood. 1990. PMID: 2265246
-
Calpain-mediated regulation of platelet signaling pathways.Curr Opin Hematol. 2007 May;14(3):249-54. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0b013e3280ef68f8. Curr Opin Hematol. 2007. PMID: 17414215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calpain regulation of integrin alpha IIb beta 3 signaling in human platelets.Platelets. 2000 Jun;11(4):189-98. doi: 10.1080/09537100050057620. Platelets. 2000. PMID: 10938897 Review.
Cited by
-
Calpain activity is negatively regulated by a KCTD7-Cullin-3 complex via non-degradative ubiquitination.Cell Discov. 2023 Mar 24;9(1):32. doi: 10.1038/s41421-023-00533-3. Cell Discov. 2023. PMID: 36964131 Free PMC article.
-
Global analysis of the rat and human platelet proteome - the molecular blueprint for illustrating multi-functional platelets and cross-species function evolution.Proteomics. 2010 Jul;10(13):2444-57. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200900271. Proteomics. 2010. PMID: 20443191 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet in thrombo-inflammation: Unraveling new therapeutic targets.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 14;13:1039843. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1039843. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36451834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of the mouse mu-calpain gene reveals an essential role in platelet function.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Mar;21(6):2213-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.6.2213-2220.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11238954 Free PMC article.
-
SNAP-23 and syntaxin-2 localize to the extracellular surface of the platelet plasma membrane.Blood. 2007 Sep 1;110(5):1492-501. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-11-055772. Epub 2007 May 7. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17485553 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Yoshida K, Dubyak G, Nachmias VT. FEBS Lett. 1986;206:273–278. - PubMed
-
- Winokur R, Hartwig JH. Blood. 1995;85:1796–1804. - PubMed
-
- Gartner TK, Gerrard JM, White JG, Williams DC. Blood. 1981;58:153–157. - PubMed
-
- Flaumenhaft R, Croce K, Chen E, Furie B, Furie BC. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:2492–2501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

