The phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase/AKT2 pathway as a critical target for farnesyltransferase inhibitor-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 10594016
- PMCID: PMC85069
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.1.139-148.2000
The phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase/AKT2 pathway as a critical target for farnesyltransferase inhibitor-induced apoptosis
Abstract
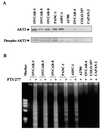
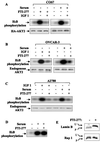
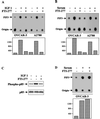
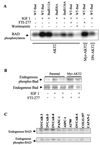
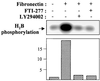
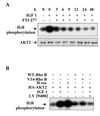
Farnesyltransferase inhibitors (FTIs) represent a novel class of anticancer drugs that exhibit a remarkable ability to inhibit malignant transformation without toxicity to normal cells. However, the mechanism by which FTIs inhibit tumor growth is not well understood. Here, we demonstrate that FTI-277 inhibits phosphatidylinositol 3-OH kinase (PI 3-kinase)/AKT2-mediated growth factor- and adhesion-dependent survival pathways and induces apoptosis in human cancer cells that overexpress AKT2. Furthermore, overexpression of AKT2, but not oncogenic H-Ras, sensitizes NIH 3T3 cells to FTI-277, and a high serum level prevents FTI-277-induced apoptosis in H-Ras- but not AKT2-transformed NIH 3T3 cells. A constitutively active form of AKT2 rescues human cancer cells from FTI-277-induced apoptosis. FTI-277 inhibits insulin-like growth factor 1-induced PI 3-kinase and AKT2 activation and subsequent phosphorylation of the proapoptotic protein BAD. Integrin-dependent activation of AKT2 is also blocked by FTI-277. Thus, a mechanism for FTI inhibition of human tumor growth is by inducing apoptosis through inhibition of PI 3-kinase/AKT2-mediated cell survival and adhesion pathway.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Farnesyltransferase inhibitors: potential role in the treatment of cancer.Drugs. 2001;61(6):723-32. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200161060-00002. Drugs. 2001. PMID: 11398905 Review.
-
Ras CAAX peptidomimetic FTI-277 selectively blocks oncogenic Ras signaling by inducing cytoplasmic accumulation of inactive Ras-Raf complexes.J Biol Chem. 1995 Nov 10;270(45):26802-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.45.26802. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7592920
-
Farnesyltransferase inhibitor effects on prostate tumor micro-environment and radiation survival.Prostate. 2005 Jan 1;62(1):69-82. doi: 10.1002/pros.20122. Prostate. 2005. PMID: 15389805
-
Cell growth inhibition by farnesyltransferase inhibitors is mediated by gain of geranylgeranylated RhoB.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Mar;19(3):1831-40. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.3.1831. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10022870 Free PMC article.
-
Farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase I inhibitors and cancer therapy: lessons from mechanism and bench-to-bedside translational studies.Oncogene. 2000 Dec 27;19(56):6584-93. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204146. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11426643 Review.
Cited by
-
Downregulation of Akt1 inhibits anchorage-independent cell growth and induces apoptosis in cancer cells.Neoplasia. 2001 Jul-Aug;3(4):278-86. doi: 10.1038/sj.neo.7900163. Neoplasia. 2001. PMID: 11571628 Free PMC article.
-
Combined effect of protein kinase B inhibitor or extracellular signal-regulated kinase inhibitor against farnesyltransferase inhibition-induced apoptosis in SiHa cells.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009 Mar;379(3):291-303. doi: 10.1007/s00210-008-0359-7. Epub 2008 Oct 15. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 18854983
-
mTOR-Independent autophagy inducer trehalose rescues against insulin resistance-induced myocardial contractile anomalies: Role of p38 MAPK and Foxo1.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Sep;111:357-373. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.06.024. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27363949 Free PMC article.
-
Farnesyltransferase inhibitors: potential role in the treatment of cancer.Drugs. 2001;61(6):723-32. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200161060-00002. Drugs. 2001. PMID: 11398905 Review.
-
Phase 2 trial of the farnesyltransferase inhibitor tipifarnib for relapsed/refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma.Blood Adv. 2024 Sep 10;8(17):4581-4592. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024012806. Blood Adv. 2024. PMID: 38991123 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ahmed N N, Franke T F, Bellacosa A, Datta K, Gonzalez-Portal M-E, Taguchi T, Testa J R, Tsichlis P N. The proteins encoded by c-akt and v-akt differ in post-translational modification, subcellular localization and oncogenic potential. Oncogene. 1993;8:1957–1963. - PubMed
-
- Alessi D R, Cohen P. Mechanism of activation and function of protein kinase B. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1998;8:55–62. - PubMed
-
- Altomare D A, Lyons G E, Mitsuuchi Y, Cheng J Q, Testa J R. Akt2 mRNA is highly expressed in embryonic brown fat and the AKT2 kinase is activated by insulin. Oncogene. 1998;16:2407–2411. - PubMed
-
- Aman M J, Lamkin T D, Okada H, Kurosaki T, Ravichandran K S. The inositol phosphatase SHIP inhibits Akt/PKB activation in B cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:33922–33928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
