The orphan nuclear receptor SHP inhibits hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 and retinoid X receptor transactivation: two mechanisms for repression
- PMID: 10594021
- PMCID: PMC85074
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.1.187-195.2000
The orphan nuclear receptor SHP inhibits hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 and retinoid X receptor transactivation: two mechanisms for repression
Abstract
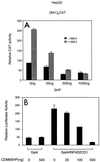
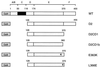
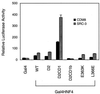
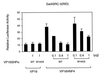
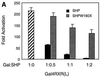
The orphan nuclear hormone receptor SHP interacts with a number of other nuclear hormone receptors and inhibits their transcriptional activity. Several mechanisms have been suggested to account for this inhibition. Here we show that SHP inhibits transactivation by the orphan receptor hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 (HNF-4) and the retinoid X receptor (RXR) by at least two mechanisms. SHP interacts with the same HNF-4 surface recognized by transcriptional coactivators and competes with them for binding in vivo. The minimal SHP sequences previously found to be required for interaction with other receptors are sufficient for interaction with HNF-4, although deletion results indicate that additional C-terminal sequences are necessary for full binding and coactivator competition. These additional sequences include those associated with direct transcriptional repressor activity of SHP. SHP also competes with coactivators for binding to ligand-activated RXR, and based on the ligand-dependent interaction with other nuclear receptors, it is likely that coactivator competition is a general feature of SHP-mediated repression. The minimal receptor interaction domain of SHP is sufficient for full interaction with RXR, as previously described. This domain is also sufficient for full coactivator competition. Functionally, however, full inhibition of RXR transactivation requires the presence of the C-terminal repressor domain, with only weak inhibition associated with this receptor interaction domain. Overall, these results suggest that SHP represses nuclear hormone receptor-mediated transactivation via two separate steps: first by competition with coactivators and then by direct effects of its transcriptional repressor function.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Novel receptor interaction and repression domains in the orphan receptor SHP.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Dec;17(12):7126-31. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.12.7126. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9372944 Free PMC article.
-
Functional domains of the human orphan receptor ARP-1/COUP-TFII involved in active repression and transrepression.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Sep;17(9):4914-32. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.9.4914. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9271371 Free PMC article.
-
Transactivation of the human apolipoprotein CII promoter by orphan and ligand-dependent nuclear receptors. The regulatory element CIIC is a thyroid hormone response element.J Biol Chem. 1998 Jul 10;273(28):17810-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.28.17810. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9651383
-
Nuclear Receptors, RXR, and the Big Bang.Cell. 2014 Mar 27;157(1):255-66. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.012. Cell. 2014. PMID: 24679540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics of coactivator recruitment and chromatin modifications during nuclear receptor mediated transcription.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008 Jan 2;280(1-2):1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2007.08.016. Epub 2007 Sep 5. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 17935877 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner is required for thiazolidinedione effects in leptin-deficient mice.J Biomed Sci. 2015 May 8;22(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12929-015-0133-3. J Biomed Sci. 2015. PMID: 25951943 Free PMC article.
-
HNF4α isoforms regulate the circadian balance between carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in the liver.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Dec 4;14:1266527. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1266527. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38111711 Free PMC article.
-
Functional role of G9a-induced histone methylation in small heterodimer partner-mediated transcriptional repression.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Nov 18;32(20):6096-103. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh947. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15550569 Free PMC article.
-
Small Heterodimer Partner Regulates Circadian Cytochromes p450 and Drug-Induced Hepatotoxicity.Theranostics. 2018 Oct 22;8(19):5246-5258. doi: 10.7150/thno.28676. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 30555544 Free PMC article.
-
All-trans-retinoic acid ameliorates hepatic steatosis in mice by a novel transcriptional cascade.Hepatology. 2014 May;59(5):1750-60. doi: 10.1002/hep.26699. Epub 2014 Mar 26. Hepatology. 2014. PMID: 24038081 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anzick S L, Kononen J, Walker R L, Azorsa D O, Tanner M M, Guan X Y, Sauter G, Kallioniemi O P, Trent J M, Meltzer P S. AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1997;277:965–968. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K, editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. J. New York, N.Y: Wiley & Sons; 1999.
-
- Bannister A J, Kouzarides T. The CBP co-activator is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature. 1996;384:641–643. - PubMed
-
- Berk A J. Activation of RNA polymerase II transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999;11:330–335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
