Regulation of a senescence checkpoint response by the E2F1 transcription factor and p14(ARF) tumor suppressor
- PMID: 10594030
- PMCID: PMC85083
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.1.273-285.2000
Regulation of a senescence checkpoint response by the E2F1 transcription factor and p14(ARF) tumor suppressor
Abstract
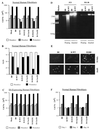
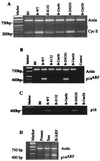
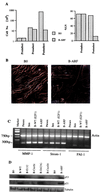
Normal cells do not divide indefinitely due to a process known as replicative senescence. Human cells arrest growth with a senescent phenotype when they acquire one or more critically short telomeres as a consequence of cell division. Recent evidence suggests that certain types of DNA damage, chromatin remodeling, and oncogenic forms of Ras or Raf can also elicit a senescence response. We show here that E2F1, a multifunctional transcription factor that binds the retinoblastoma (pRb) tumor suppressor and that can either promote or suppress tumorigenesis, induces a senescent phenotype when overexpressed in normal human fibroblasts. Normal human cells stably arrested proliferation and expressed several markers of replicative senescence in response to E2F1. This activity of E2F1 was independent of its pRb binding activity but dependent on its ability to stimulate gene expression. The E2F1 target gene critical for the senescence response appeared to be the p14(ARF) tumor suppressor. Replicatively senescent human fibroblasts overexpressed p14(ARF), and ectopic expression of p14(ARF) in presenescent cells induced a phenotype similar to that induced by E2F1. Consistent with a critical role for p14(ARF), cells with compromised p53 function were immune to senescence induction by E2F1, as were cells deficient in p14(ARF). Our findings support the idea that the senescence response is a critical tumor-suppressive mechanism, provide an explanation for the apparently paradoxical roles of E2F1 in oncogenesis, and identify p14(ARF) as a potentially important mediator of the senescent phenotype.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Induction of apoptosis in human esophageal cancer cells by sequential transfer of the wild-type p53 and E2F-1 genes: involvement of p53 accumulation via ARF-mediated MDM2 down-regulation.Clin Cancer Res. 2000 Jul;6(7):2851-9. Clin Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10914734
-
The helix-loop-helix protein Id-1 and a retinoblastoma protein binding mutant of SV40 T antigen synergize to reactivate DNA synthesis in senescent human fibroblasts.Dev Genet. 1996;18(2):161-72. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6408(1996)18:2<161::AID-DVG9>3.0.CO;2-7. Dev Genet. 1996. PMID: 8934878
-
p14(ARF) regulates E2F activity.Oncogene. 2002 Jun 20;21(27):4220-30. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205524. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12082609
-
The cellular effects of E2F overexpression.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1996;208:79-93. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-79910-5_4. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8575214 Review.
-
The role of the transcription factor DP in apoptosis.Apoptosis. 2003 Oct;8(5):461-8. doi: 10.1023/a:1025586207239. Apoptosis. 2003. PMID: 12975577 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantifying E2F1 protein dynamics in single cells.Quant Biol. 2020 Mar;8(1):20-30. doi: 10.1007/s40484-019-0193-6. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Quant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32542116 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming of microRNA expression via E2F1 downregulation promotes Salmonella infection both in infected and bystander cells.Nat Commun. 2021 Jun 7;12(1):3392. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23593-z. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34099666 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Studies on Primary Tubular Epithelial Cells Indicate a Tumor Suppressor Role of SETD2 in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Neoplasia. 2016 Jun;18(6):339-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2016.04.005. Epub 2016 May 26. Neoplasia. 2016. PMID: 27292023 Free PMC article.
-
Erk1 and Erk2 regulate endothelial cell proliferation and migration during mouse embryonic angiogenesis.PLoS One. 2009 Dec 14;4(12):e8283. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008283. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 20011539 Free PMC article.
-
Ectopic expression of E2F1 stimulates beta-cell proliferation and function.Diabetes. 2010 Jun;59(6):1435-44. doi: 10.2337/db09-1295. Epub 2010 Mar 18. Diabetes. 2010. PMID: 20299467 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afshari C A, Vojta P J, Annab L A, Futreal P A, Willard T B, Barrett J C. Investigation of the role of G1/S cell cycle mediators in cellular senescence. Exp Cell Res. 1993;209:231–237. - PubMed
-
- Bates S, Phillips A C, Clark P A, Stott F, Peters G, Ludwig R L, Voudsen K H. p14ARF links the tumor suppressors RB and p53. Nature. 1998;395:124–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
