Activated mutants of SHP-2 preferentially induce elongation of Xenopus animal caps
- PMID: 10594032
- PMCID: PMC85085
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.1.299-311.2000
Activated mutants of SHP-2 preferentially induce elongation of Xenopus animal caps
Abstract
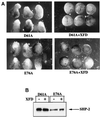
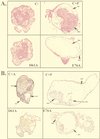
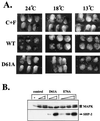
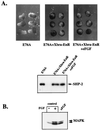
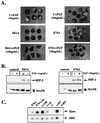
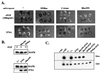
In Xenopus ectodermal explants (animal caps), fibroblast growth factor (FGF) evokes two major events: induction of ventrolateral mesodermal tissues and elongation. The Xenopus FGF receptor (XFGFR) and certain downstream components of the XFGFR signal transduction pathway (e.g., members of the Ras/Raf/MEK/mitogen-activated protein kinase [MAPK] cascade) are required for both of these processes. Likewise, activated versions of these signaling components induce mesoderm and promote animal cap elongation. Previously, using a dominant negative mutant approach, we showed that the protein-tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 is necessary for FGF-induced MAPK activation, mesoderm induction, and elongation of animal caps. Taking advantage of recent structural information, we now have generated novel, activated mutants of SHP-2. Here, we show that expression of these mutants induces animal cap elongation to an extent comparable to that evoked by FGF. Surprisingly, however, activated mutant-induced elongation can occur without mesodermal cytodifferentiation and is accompanied by minimal activation of the MAPK pathway and mesodermal marker expression. Our results implicate SHP-2 in a pathway(s) directing cell movements in vivo and identify potential downstream components of this pathway. Our activated mutants also may be useful for determining the specific functions of SHP-2 in other signaling systems.
Figures
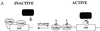
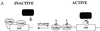
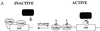
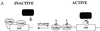


References
-
- Allard J D, Chang H C, Herbst R, McNeill H, Simon M A. The SH2-containing tyrosine phosphatase corkscrew is required during signaling by sevenless, Ras1 and Raf. Development. 1996;122:1137–1146. - PubMed
-
- Amaya E, Musci T J, Kirschner M W. Expression of a dominant negative mutant of the FGF receptor disrupts mesoderm formation in Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1991;66:257–260. - PubMed
-
- Barford D, Neel B G. Revealing mechanisms for SH2 domain-mediated regulation of the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2. Structure. 1998;6:249–254. - PubMed
-
- Barrett K, Leptin M, Settleman J. The Rho GTPase and a putative RhoGEF mediate a signaling pathway for the cell shape changes in Drosophila gastrulation. Cell. 1997;91:905–915. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
