The drosophila MSL complex acetylates histone H4 at lysine 16, a chromatin modification linked to dosage compensation
- PMID: 10594033
- PMCID: PMC85086
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.1.312-318.2000
The drosophila MSL complex acetylates histone H4 at lysine 16, a chromatin modification linked to dosage compensation
Abstract
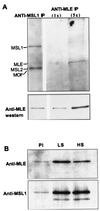
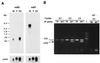
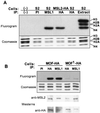
In Drosophila, dosage compensation-the equalization of most X-linked gene products in males and females-is achieved by a twofold enhancement of the level of transcription of the X chromosome in males relative to each X chromosome in females. A complex consisting of at least five gene products preferentially binds the X chromosome at numerous sites in males and results in a significant increase in the presence of a specific histone isoform, histone 4 acetylated at lysine 16. Recently, RNA transcripts (roX1 and roX2) encoded by two different genes have also been found associated with the X chromosome in males. We have partially purified a complex containing MSL1, -2, and -3, MOF, MLE, and roX2 RNA and demonstrated that it exclusively acetylates H4 at lysine 16 on nucleosomal substrates. These results demonstrate that the MSL complex is responsible for the specific chromatin modification characteristic of the X chromosome in Drosophila males.
Figures


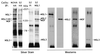
Similar articles
-
Targeting of MOF, a putative histone acetyl transferase, to the X chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster.Dev Genet. 1998;22(1):56-64. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6408(1998)22:1<56::AID-DVG6>3.0.CO;2-6. Dev Genet. 1998. PMID: 9499580
-
The roX genes encode redundant male-specific lethal transcripts required for targeting of the MSL complex.EMBO J. 2002 Mar 1;21(5):1084-91. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.5.1084. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 11867536 Free PMC article.
-
roX RNAs are required for increased expression of X-linked genes in Drosophila melanogaster males.Genetics. 2006 Dec;174(4):1859-66. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.064568. Epub 2006 Oct 8. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 17028315 Free PMC article.
-
Dosage compensation and chromatin structure in Drosophila.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996 Aug;6(4):496-501. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(96)80073-6. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996. PMID: 8791531 Review.
-
The right dose for every sex.Chromosoma. 2007 Apr;116(2):95-106. doi: 10.1007/s00412-006-0089-x. Epub 2006 Nov 24. Chromosoma. 2007. PMID: 17124606 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chromosome-wide gene-specific targeting of the Drosophila dosage compensation complex.Genes Dev. 2006 Apr 1;20(7):858-70. doi: 10.1101/gad.1399406. Epub 2006 Mar 17. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16547172 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast SAS (something about silencing) protein complex contains a MYST-type putative acetyltransferase and functions with chromatin assembly factor ASF1.Genes Dev. 2001 Dec 1;15(23):3155-68. doi: 10.1101/gad.907201. Genes Dev. 2001. PMID: 11731479 Free PMC article.
-
The MLE subunit of the Drosophila MSL complex uses its ATPase activity for dosage compensation and its helicase activity for targeting.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Feb;28(3):958-66. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00995-07. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18039854 Free PMC article.
-
Functional integration of the histone acetyltransferase MOF into the dosage compensation complex.EMBO J. 2004 Jun 2;23(11):2258-68. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600235. Epub 2004 May 13. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15141166 Free PMC article.
-
New perspectives for the regulation of acetyltransferase MOF.Epigenetics. 2010 Apr;5(3):185-8. doi: 10.4161/epi.5.3.11372. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Epigenetics. 2010. PMID: 20305383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amrein H, Axel R. Genes expressed in neurons of adult male Drosophila. Cell. 1997;88:459–469. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner M. Drosophila: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1989.
-
- Ausio J, van Holde K E. Histone hyperacetylation: its effects on nucleosome conformation and stability. Biochemistry. 1986;25:1421–1428. - PubMed
-
- Bashaw G J, Baker B S. The msl-2 dosage compensation gene of Drosophila encodes a putative DNA-binding protein whose expression is sex specifically regulated by Sex-lethal. Development. 1995;121:3245–3258. - PubMed
-
- Bashaw G J, Baker B S. The regulation of the Drosophila msl-2 gene reveals a function for Sex-lethal in translational control. Cell. 1997;89:789–798. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
