E2F is required to prevent inappropriate S-phase entry of mammalian cells
- PMID: 10594038
- PMCID: PMC85091
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.1.363-371.2000
E2F is required to prevent inappropriate S-phase entry of mammalian cells
Abstract
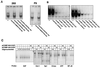
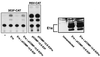
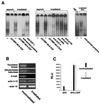
E2F is a family of transcription factors that regulates the cell cycle. It is widely accepted that E2F-mediated transactivation of a set of genes is the critical activity that governs cellular progression through G(1) into S phase. In contrast to this hypothesis, we demonstrate that E2F actually suppresses the onset of S phase in two cell types when the cells are arrested by gamma irradiation. Our findings indicate that in these cells, the critical event triggering progression from G(0)/G(1) arrest into S phase is the release of E2F-mediated transrepression of cell cycle genes, not transactivation by E2F. Furthermore, our data suggest that E2F-mediated transactivation is not necessary for the G(1)/S-phase transition in these cells.
Figures

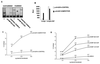
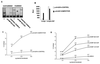
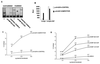

Similar articles
-
Deregulated expression of E2F family members induces S-phase entry and overcomes p16INK4A-mediated growth suppression.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Mar;16(3):1047-57. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.3.1047. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8622649 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the cdk inhibitor p21 gene during cell cycle progression is under the control of the transcription factor E2F.Oncogene. 1998 Mar 26;16(12):1513-23. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201667. Oncogene. 1998. PMID: 9569018
-
Protein-DNA interactions at the major and minor promoters of the divergently transcribed dhfr and rep3 genes during the Chinese hamster ovary cell cycle.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Feb;16(2):634-47. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.2.634. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8552092 Free PMC article.
-
E2F target genes and cell-cycle checkpoint control.Bioessays. 1999 Mar;21(3):221-30. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199903)21:3<221::AID-BIES6>3.0.CO;2-J. Bioessays. 1999. PMID: 10333731 Review.
-
Regulation of the G1/S transition phase in mesangial cells by E2F1.Kidney Int. 1999 Oct;56(4):1238-41. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.1999.00705.x. Kidney Int. 1999. PMID: 10504464 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomaterials for Mimicking and Modelling Tumor Microenvironment.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1379:139-170. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-04039-9_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35760991 Review.
-
Targeting the Retinoblastoma/E2F repressive complex by CDK4/6 inhibitors amplifies oncolytic potency of an oncolytic adenovirus.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 10;13(1):4689. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32087-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35948546 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing roles for ATF2 and c-Fos in c-Jun-mediated neuronal apoptosis.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 May;29(9):2431-42. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01344-08. Epub 2009 Mar 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19255142 Free PMC article.
-
RhoA signaling modulates cyclin D1 expression in human lung fibroblasts; implications for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Respir Res. 2006 Jun 15;7(1):88. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-7-88. Respir Res. 2006. PMID: 16776827 Free PMC article.
-
MAT1-modulated CAK activity regulates cell cycle G(1) exit.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Jan;21(1):260-70. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.1.260-270.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11113200 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagchi S, Raychaudhuri P, Nevins J R. Adenovirus E1A proteins can dissociate heteromeric complexes involving the E2F transcription factor: a novel mechanism for E1A transactivation. Cell. 1990;62:659–669. - PubMed
-
- Bielinska A, Shivdasani R A, Zhang L Q, Nabel G J. Regulation of gene expression with double-stranded phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. Science. 1990;250:997–1000. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
