DNA binding site selection of dimeric and tetrameric Stat5 proteins reveals a large repertoire of divergent tetrameric Stat5a binding sites
- PMID: 10594041
- PMCID: PMC85094
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.1.389-401.2000
DNA binding site selection of dimeric and tetrameric Stat5 proteins reveals a large repertoire of divergent tetrameric Stat5a binding sites
Abstract
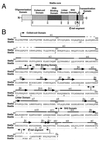
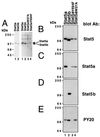
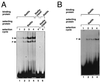
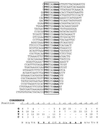
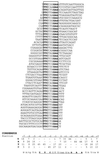
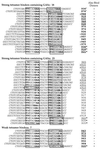
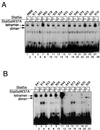
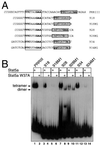
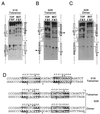
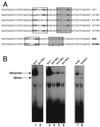
We have defined the optimal binding sites for Stat5a and Stat5b homodimers and found that they share similar core TTC(T/C)N(G/A)GAA interferon gamma-activated sequence (GAS) motifs. Stat5a tetramers can bind to tandemly linked GAS motifs, but the binding site selection revealed that tetrameric binding also can be seen with a wide range of nonconsensus motifs, which in many cases did not allow Stat5a binding as a dimer. This indicates a greater degree of flexibility in the DNA sequences that allow binding of Stat5a tetramers than dimers. Indeed, in an oligonucleotide that could bind both dimers and tetramers, it was possible to design mutants that affected dimer binding without affecting tetramer binding. A spacing of 6 bp between the GAS sites was most frequently selected, demonstrating that this distance is favorable for Stat5a tetramer binding. These data provide insights into tetramer formation by Stat5a and indicate that the repertoire of potential binding sites for this transcription factor is broader than expected.
Figures




References
-
- Baldwin A S J. Methylation interference assay for analysis of DNA-protein interactions. In: Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K, editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. Vol. 2. New York, N.Y: Greene Publishing Associates/Wiley-Interscience; 1987. pp. 12.3.1–12.3.4. - PubMed
-
- Becker S, Groner B, Muller C W. Three-dimensional structure of the Stat3β homodimer bound to DNA. Nature. 1998;394:145–151. - PubMed
-
- Bergad P L, Shih H-M, Towle H C, Schwarzenberg S J, Berry S A. Growth hormone induction of hepatic serine protease inhibitor 2.1 transcription is mediated by a Stat5-related factor binding synergistically to two γ-activated sites. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:24903–24910. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
