Differences in expression of acetylcholinesterase and collagen Q control the distribution and oligomerization of the collagen-tailed forms in fast and slow muscles
- PMID: 10594051
- PMCID: PMC6784926
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-24-10672.1999
Differences in expression of acetylcholinesterase and collagen Q control the distribution and oligomerization of the collagen-tailed forms in fast and slow muscles
Abstract
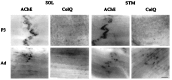
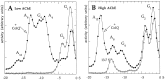
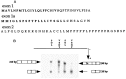
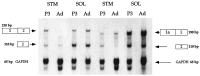
The collagen-tailed forms of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) are accumulated at mammalian neuromuscular junctions. The A(4), A(8), and A(12) forms are expressed differently in the rat fast and slow muscles; the sternomastoid muscle contains essentially the A(12) form at end plates, whereas the soleus muscle also contains extrajunctional A(4) and A(8) forms. We show that collagen Q (ColQ) transcripts become exclusively junctional in the adult sternomastoid but remain uniformly expressed in the soleus. By coinjecting Xenopus oocytes with AChE(T) and ColQ mRNAs, we reproduced the muscle patterns of collagen-tailed forms. The soleus contains transcripts ColQ1 and ColQ1a, whereas the sternomastoid only contains ColQ1a. Collagen-tailed AChE represents the first evidence that synaptic components involved in cholinergic transmission may be differently regulated in fast and slow muscles.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The asymmetric molecular forms of AChE and the expression of collagen Q in mature and immature fast and slow rat muscles.Chem Biol Interact. 2010 Sep 6;187(1-3):90-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2010.02.034. Epub 2010 Feb 25. Chem Biol Interact. 2010. PMID: 20188715
-
Expression of cAMP-responsive element binding proteins (CREBs) in fast- and slow-twitch muscles: a signaling pathway to account for the synaptic expression of collagen-tailed subunit (ColQ) of acetylcholinesterase at the rat neuromuscular junction.Chem Biol Interact. 2013 Mar 25;203(1):282-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2012.10.025. Epub 2012 Nov 15. Chem Biol Interact. 2013. PMID: 23159887
-
Transcriptional regulation of acetylcholinesterase-associated collagen ColQ: differential expression in fast and slow twitch muscle fibers is driven by distinct promoters.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jun 25;279(26):27098-107. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M402596200. Epub 2004 Apr 21. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15102835
-
Acetylcholinesterase in the neuromuscular junction.Chem Biol Interact. 1999 May 14;119-120:301-8. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(99)00040-x. Chem Biol Interact. 1999. PMID: 10421465 Review.
-
The polymorphism of acetylcholinesterase: post-translational processing, quaternary associations and localization.Chem Biol Interact. 1999 May 14;119-120:29-42. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(99)00011-3. Chem Biol Interact. 1999. PMID: 10421436 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Innervation as an Experimental Model to Study the Expression and Functions of Acetylcholinesterase and Agrin in Human Skeletal Muscle.Molecules. 2017 Aug 27;22(9):1418. doi: 10.3390/molecules22091418. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28846617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MuSK is required for anchoring acetylcholinesterase at the neuromuscular junction.J Cell Biol. 2004 May 24;165(4):505-15. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200307164. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15159418 Free PMC article.
-
Dissociation of transcription, translation, and assembly of collagen-tailed acetylcholinesterase in skeletal muscle.J Biol Chem. 2009 Aug 7;284(32):21488-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.030049. Epub 2009 Jun 9. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19509281 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Assembly and Biosynthesis of Acetylcholinesterase in Brain and Muscle: the Roles of t-peptide, FHB Domain, and N-linked Glycosylation.Front Mol Neurosci. 2011 Oct 25;4:36. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2011.00036. eCollection 2011. Front Mol Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22046147 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-MuSK autoantibodies block binding of collagen Q to MuSK.Neurology. 2011 Nov 15;77(20):1819-26. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318237f660. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Neurology. 2011. PMID: 22013178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bon S, Massoulié J. Quaternary associations of acetylcholinesterase. I. Oligomeric associations of T subunits with and without the amino-terminal domain of the collagen tail. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:3007–3015. - PubMed
-
- Bon S, Cartaud J, Massoulié J. The dependence of acetylcholinesterase aggregation at low ionic strength upon a polyanionic component. Eur J Biochem. 1978;85:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Bon S, Coussen F, Massoulié J. Quaternary associations of acetylcholinesterase. II. The polyproline attachment domain of the collagen tail. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:3016–3021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
