Involvement of cajal-retzius neurons in spontaneous correlated activity of embryonic and postnatal layer 1 from wild-type and reeler mice
- PMID: 10594067
- PMCID: PMC6784924
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-24-10856.1999
Involvement of cajal-retzius neurons in spontaneous correlated activity of embryonic and postnatal layer 1 from wild-type and reeler mice
Abstract
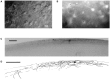
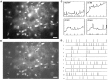
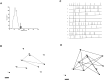
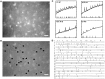
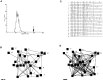
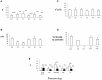
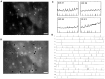
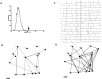
Cajal-Retzius (CR) cells are a transient population of neurons in developing cortical layer 1 that secrete reelin, a protein necessary for cortical lamination. Combining calcium imaging of cortical hemispheres and cross-correlation analysis, we previously found spontaneous correlated activity among non-CR neurons in postnatal rat layer 1. This correlated activity was blocked by GABAergic and glutamatergic antagonists, and we postulated that it was controlled by CR cells. We now investigate the correlated activity of embryonic and postnatal layer 1 in wild-type and reeler mice, mutant in the production of reelin. We find that mouse layer 1 also sustains patterned spontaneous activity and that CR cells participate in correlated networks. These networks are present in embryonic marginal zone and are blocked by GABAergic and glutamatergic antagonists. Surprisingly, network activity in reeler mice displays similar characteristics and pharmacological profile as in wild-type mice, although small differences are detected. Our results demonstrate that the embryonic marginal zone has correlated spontaneous activity that could serve as the scaffold for the development of intracortical connections. Our data also suggest that reelin does not have a major impact in the development of specific synaptic circuits in layer 1.
Figures
References
-
- Berridge MJ. Neuronal calcium signaling. Neuron. 1998;21:13–26. - PubMed
-
- Cauller LJ, Kulics AT. The neural basis of the behaviourally relevant N1 component of the somatosensory-evoked potentials of S1 cortex of awake monkeys: evidence that backward cortical projection signals conscius touch sensation. Exp Brain Res. 1991;84:607–619. - PubMed
-
- Caviness VSJ, Sidman RL. Time of origin of corresponding cell classes in the cerebral cortex of normal and mutant reeler mice: an autoradiographic analysis. J Comp Neurol. 1973;148:141–151. - PubMed
-
- D'Arcangelo G, Miao GG, Chen S-C, Soarse HD, Morgan JI, Curran T. A protein related to extracellular matrix proteins deleted in the mouse mutant reeler. Nature. 1995;374:719–723. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
