Proprioceptive control of extensor activity during fictive scratching and weight support compared to fictive locomotion
- PMID: 10594077
- PMCID: PMC6784935
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-24-10966.1999
Proprioceptive control of extensor activity during fictive scratching and weight support compared to fictive locomotion
Abstract
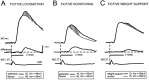
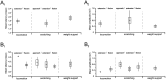
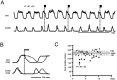
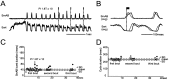
At rest, extensor group I afferents produce oligosynaptic inhibition of extensor motoneurons. During locomotor activity, however, such inhibition is replaced by oligosynaptic excitation. Oligosynaptic excitation from extensor group I afferents plays a crucial role in the regulation of extensor activity during walking. In this study we investigate the possibility that this mechanism also regulates extensor muscle activity during other motor tasks. We show that the reflex pathways responsible for extensor group I oligosynaptic excitation during fictive locomotion can be activated during both fictive scratching and fictive weight support (tonic motor activity induced by contralateral scratching). These observations suggest that the excitatory group I oligosynaptic reflex pathways are open for transmission during several forms of motor activities. We also show that extensor group I input during fictive scratching can affect the amplitude and the timing of extensor activity in a pattern similar to that observed during locomotion. Most likely these effects involve the activation of the excitatory group I oligosynaptic reflex pathways. Accordingly, it is suggested that extensor group I oligosynaptic excitation during motor activities other than locomotion is also used to regulate extensor muscle activity. Furthermore, the similarity of effects from extensor group I input on the rhythmicity during scratching and locomotion supports the hypothesis that both rhythms are generated by a common network.
Figures



References
-
- Baev KV, Kostyuk PG. Primary afferent depolarisation evoked by the activity of spinal scratching generator. Neuroscience. 1981;6:205–215. - PubMed
-
- Baev KV, Esipenko VB, Shimansky YP. Afferent control of central pattern generators: experimental analysis of scratching in the decerebrate cat. Neuroscience. 1991;40:239–256. - PubMed
-
- Berkinblit MB, Deliagina TG, Orlovsky GN, Feldman AG. Activity of motoneurons during fictitious scratch reflex in the cat. Brain Res. 1980;193:427–438. - PubMed
-
- Brownstone RM, Gossard JP, Hultborn H. Voltage-dependent excitation of motoneurones from spinal locomotor centres in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1994;102:34–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
