Elevated levels of beta-chemokines in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of individuals infected with human T lymphotropic virus type-1 (HTLV-1)
- PMID: 10594561
- PMCID: PMC1905436
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.01093.x
Elevated levels of beta-chemokines in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of individuals infected with human T lymphotropic virus type-1 (HTLV-1)
Abstract
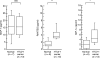
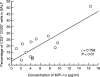
Pulmonary complications are known to develop in HTLV-1 carriers, including T lymphocytic alveolitis, and increased IL-2 receptor alpha (CD25)-bearing T cells have been found in BALF. Several chemokines may contribute to accumulation of T lymphocytes in the lungs of HTLV-1 carriers. Here, we compared the distribution of T lymphocyte subsets and beta-chemokines, such as macrophage inflammatory peptide-1alpha (MIP-1alpha), regulated on activation normal T expressed and secreted (RANTES), and macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), in BALF and peripheral blood between HTLV-1 carriers and non-infected healthy normal subjects. Flow cytometric analysis with MoAbs to cell surface antigens was used to identify T lymphocyte subsets in BALF samples from HTLV-1 carriers (n = 13) and non-infected healthy controls (n = 10). The levels of different beta-chemokines were estimated by ELISA. High percentages of CD3+ cells, CD3 expressing HLA-DR antigen and CD3+CD25+ cells were detected in BALF of HTLV-1 carriers compared with non-infected controls. The concentration of MIP-1alpha in BALF of patients was significantly higher than in non-infected healthy controls and correlated well with the percentage of CD3+CD25+ cells. The level of RANTES in BALF was also significantly high in HTLV-1 carriers, but did not correlate with the percentage of CD3+CD25+ cells. On the other hand, the level of MCP-1 in BALF of HTLV-1 carriers was not different from that of controls. Our results suggest a possible interaction between activated T cells bearing CD25 and beta-chemokines, especially MIP-1alpha, which may contribute to the pulmonary involvement in HTLV-1 carriers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elevated levels of soluble adhesion molecules in sera and BAL fluid of individuals infected with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1.Chest. 2000 Dec;118(6):1754-61. doi: 10.1378/chest.118.6.1754. Chest. 2000. PMID: 11115469
-
High concentrations of beta-chemokines in BAL fluid of patients with diffuse panbronchiolitis.Chest. 2001 Aug;120(2):602-7. doi: 10.1378/chest.120.2.602. Chest. 2001. PMID: 11502665
-
Analysis of T cell subsets and beta chemokines in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis.Thorax. 1997 May;52(5):431-7. doi: 10.1136/thx.52.5.431. Thorax. 1997. PMID: 9176534 Free PMC article.
-
[Deep lung--cellular reaction to HIV].Rev Port Pneumol. 2007 Mar-Apr;13(2):175-212. Rev Port Pneumol. 2007. PMID: 17492233 Review. Portuguese.
-
The role of chemokines in the pathogenesis of scleroderma.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003 Nov;15(6):772-7. doi: 10.1097/00002281-200311000-00015. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003. PMID: 14569209 Review.
Cited by
-
An Overview of Human T-Lymphotropic Virus Type 1 Lung Injury.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 1;13:914498. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.914498. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35844492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 Changes Leukocyte Number and Oxidative Stress in the Lung and Blood of Female BALB/c Mice.Adv Biomed Res. 2021 Jan 30;10:6. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_117_20. eCollection 2021. Adv Biomed Res. 2021. PMID: 33959563 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced inhibition of lymphocyte activation by Mycobacterium avium complex in human T lymphotrophic virus type I carriers.Thorax. 2001 May;56(5):394-7. doi: 10.1136/thorax.56.5.394. Thorax. 2001. PMID: 11312409 Free PMC article.
-
Human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1 associated pulmonary disease: clinical and pathological features of an under-recognised complication of HTLV-1 infection.Retrovirology. 2021 Jan 6;18(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12977-020-00543-z. Retrovirology. 2021. PMID: 33407607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic rhinitis in HTLV-1 carriers: a histopathologic study.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2012 Apr;78(2):35-40. doi: 10.1590/S1808-86942012000200007. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2012. PMID: 22499368 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Watanabe T. HTLV-1-associated diseases. Int J Hematol. 1997;66:257–78. - PubMed
-
- Vermont JC, Buisson G, Magdeleine J, et al. T-lymphocyte alveolitis, tropic spastic paresis and Sjögren syndrome. Lancet. 1988;i - PubMed
-
- Sugimoto M, Nakashima H, Watanabe S, et al. T-lymphocyte alveolitis in HTLV-1-associated myelopathy. Lancet. 1987;ii - PubMed
-
- Couderc LI, Caubarrere I, Venet A, et al. Bronchoalveolar lymphocytosis in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis associated with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 (HTLV-1): clinical, immunologic, and cytologic studies. Ann Intern Med. 1988;109:625–8. - PubMed
-
- Maruyama M, Tihara J, Sakashita I, et al. HTLV-1-associated bronchopneumopathy: a new clinical entity? Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988;137
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

