Effects of cocaine administration to influenza virus-immunized mice on cytokine profiles of individual splenic CD4+ and CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 10594563
- PMCID: PMC1905446
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.01074.x
Effects of cocaine administration to influenza virus-immunized mice on cytokine profiles of individual splenic CD4+ and CD8+ T cells
Abstract
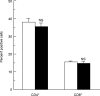
We have analysed the effects of cocaine, administered to mice during the in vivo differentiation of effector T cells stimulated by antigen (influenza virus) recognition, on the frequency of IL-2-, IL-4- and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma)-expressing CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Each animal was injected intraperitoneally with 10 mg/kg of cocaine 6, 24, 48 and 72 h after immunization with A/PR8 influenza virus (PR8). This enabled the determination of the pharmacological effects of cocaine on T cells during the initial step of the immune response, which is characterized by the production of large amounts of immunoregulatory cytokines. The distribution of IL-2-, IL-4- and IFN-gamma-producing CD4+ and CD8+ T cells was assayed on unseparated PR8-immune spleen cells, obtained from mice treated with cocaine or vehicle, and restimulated in vitro with UV-inactivated PR8 virus. The frequency of T cells singly or co-expressing the above three cytokines was determined at single-cell level by simultaneous flow cytometric analysis of intracellular cytokines and surface antigen expression. In parallel, the levels of IL-2, IL-4 and IFN-gamma in the culture supernatants were quantified by ELISA. The results showed that cocaine, administered during the in vivo virus-induced differentiation of T cells, caused an increase of both the frequencies of CD8+ T cells singly and co-expressing IL-2 and IFN-gamma and the levels of these cytokines in virus-restimulated spleen cell culture supernatants, compared with those of untreated controls. In contrast, no effect was found on IL-4-positive CD8+ T cells and on IL-2-, IFN-gamma- and IL-4-positive CD4+ T cells. Our findings suggest that the immunomodulatory effects of cocaine may be due to the up-regulation of the production of IL-2 and IFN-gamma by CD8+ T cells with a type 0 cytokine profile.
Figures
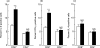
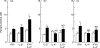
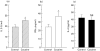
References
-
- Pellegrino T, Bayer MB. In vivo effects of cocaine on immune cell function. J Neuroimmunol. 1998;83:139–47. - PubMed
-
- Watzl B, Chen G, Scuderi P, Pirozhkov S, Watson RR. Cocaine-induced suppression of interferon-gamma secretion in leukocytes from young and old C57BL/6 mice. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1992;14:1125–31. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Huang DS, Watson RR. In vitro and in vivo cocaine modulation on production of cytokine in C57BL/6 mice. Life Sci. 1994;54:401–11. - PubMed
-
- Mao JT, Huang M, Wang J, Sharma S, Tashkin DP, Dubinett SM. Cocaine down-regulates IL2-induced peripheral blood lymphocytes IL8 and IFN-γ production. Cell Immunol. 1996;172:217–23. - PubMed
-
- Falchetti R, Di Francesco P, Lanzilli G, Gaziano R, Casalinuovo IA, Ravagnan G, Garaci E. In vitro effects of cocaine on cytokine secretion induced in murine splenic CD4+ T cells by antigen-specific stimulation. Cell Immunol. 1995;164:57–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

