Familial encephalopathy with neuroserpin inclusion bodies
- PMID: 10595921
- PMCID: PMC3277299
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65510-1
Familial encephalopathy with neuroserpin inclusion bodies
Abstract
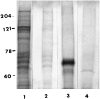
We report on a new familial neurodegenerative disease with associated dementia that has presented clinically in the fifth decade, in both genders, and in each of several generations of a large family from New York State-a pattern of inheritance consistent with an autosomal dominant mode of transmission. A key pathological finding is the presence of neuronal inclusion bodies distributed throughout the gray matter of the cerebral cortex and in certain subcortical nuclei. These inclusions are distinct from any described previously and henceforth are identified as Collins bodies. The Collins bodies can be isolated by simple biochemical procedures and have a surprisingly simple composition; neuroserpin (a serine protease inhibitor) is their predominant component. An affinity-purified antibody against neuroserpin specifically labels the Collins bodies, confirming their chemical composition. Therefore, we propose a new disease entity-familial encephalopathy with neuroserpin inclusion bodies (FENIB). The conclusion that FENIB is a previously unrecognized neurodegenerative disease is supported by finding Collins bodies in a small kindred from Oregon with familial dementia who are unrelated to the New York family. The autosomal dominant inheritance strongly suggests that FENIB is caused by mutations in the neuroserpin gene, resulting in intracellular accumulation of the mutant protein.
Figures
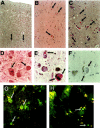






 ); clinically (
); clinically ( );
or neuropathologically
(⋄).
Unaffected individuals are indicated by open symbols
(⋄).
The pedigree has been modified to protect the family’s privacy.
Deceased individuals are not indicated. Roman numerals refer to the
generation, Arabic numbers to individuals within that
generation.
);
or neuropathologically
(⋄).
Unaffected individuals are indicated by open symbols
(⋄).
The pedigree has been modified to protect the family’s privacy.
Deceased individuals are not indicated. Roman numerals refer to the
generation, Arabic numbers to individuals within that
generation.References
-
- Hardy J, Gwinn-Hardy K: Genetic classification of primary neurodegenerative disease. Science 1998, 282:1075-1079 - PubMed
-
- Price DL, Sisodia SS, Borchelt DR: Genetic neurodegenerative disease: the human illness and transgenic models. Science 1998, 282:1079-1083 - PubMed
-
- Muller U, Graeber MB: Neurogenetic diseases: molecular diagnosis and therapeutic approaches. J Mol Med 1996, 74:71-84 - PubMed
-
- Giannakopoulos P, Hof PR, Savioz A, Guimon J, Antonarakis SE, Bouras C: Early-onset dementias: clinical, neuropathological and genetic characteristics. Acta Neuropathol 1996, 91:451-465 - PubMed
-
- Hart MN: Contributions of autopsy to modern neurologic science. Hill RB Anderson RE eds. The Autopsy: Medical Practice and Public Policy. 1988, :pp 91-105 Butterworths, Boston
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

