Somatic mutations of the L12a gene in V-kappa(1) light chain deposition disease: potential effects on aberrant protein conformation and deposition
- PMID: 10595931
- PMCID: PMC1866929
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)65520-4
Somatic mutations of the L12a gene in V-kappa(1) light chain deposition disease: potential effects on aberrant protein conformation and deposition
Abstract
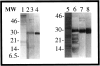
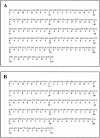
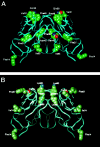
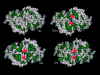
Light chain deposition disease (LCDD) and light chain amyloidosis (AL) are disorders of monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition in which normally soluble serum precursors form insoluble deposits in tissues. A common feature in both is the clonal proliferation of B-cells that produce pathogenic light chains. However, the deposits in LCDD differ from those in AL in that they are ultrastructurally granular rather than fibrillar and do not bind Congo red or colocalize with amyloid P component or apolipoprotein E. The reason(s) for their differences are unknown but are likely multifactorial and related to their protein conformation and their interaction with other molecules and tissue factors in the microenvironment. Knowledge of the primary structure of the light chains in LCDD is very limited. In the present study two new kappa(1) light chains from patients with LCDD are described and compared to seven other reported kappa-LCDD proteins. The N-terminal amino acid sequences of light chain GLA extracted from the renal biopsy and light chain CHO from myocardial tissue were each identical to the respective light chains isolated from the urines and to the V-region amino acid sequences translated from the cloned cDNAs obtained from bone marrow cells. The germline V-region sequences, determined from the genomic DNA in both and in MCM, a previously reported kappa(1) LCDD light chain, were identical and related to the L12a germline gene. The expressed light chains in all three exhibit amino acid substitutions that arise from somatic mutation and result in increased hydrophobicity with the potential for protein destabilization and disordered conformation.
Figures


References
-
- Gallo G, Picken M, Buxbaum J, Frangione B: The spectrum of monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition disease associated with immunocytic dyscrasias. Semin Hematol 1989, 3:234-245 - PubMed
-
- Lyon AW, Narindrasorasak S, Young ID, Anastassiades T, Couchman JR, McCarthy KJ, Kisilevsky R: Co-deposition of basement membrane components during the induction of murine splenic AA amyloid. Lab Invest 1991, 64:785-790 - PubMed
-
- Randall RE, Williamson WC, Jr, Mulinax F, Tung MY, Still MJ: Manifestations of systemic light chain deposition. Am J Med 1976, 60:293-299 - PubMed
-
- Ganeval D, Mignon F, Preud’homme JL, Noel L-H, Morel-Maroger L, Droz D, Brouet JC, Mery J, Grunfeld J-P: Visceral deposition of monoclonal light chains and immunoglobulins: a study of renal and immunopathologic abnormalities. Adv Nephrol 1982, 11:25-63
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

